
Soap Bubbles in Equilibrium
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 31
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 31
 4-9-2016
4-9-2016
 2206
2206
Soap Bubbles in Equilibrium
Two soap bubbles of radius R0 are connected by a thin “straw” of negligible volume compared to the volume of the bubbles (see Figure 1.1). The ambient pressure is Pa, the temperature is τ, and the surface tension coefficient is σ.
a) Is this system in stable equilibrium? What is the final state?
b) Calculate the entropy change between the final-state configuration and the configuration in Figure 1.1. Assume 2σ/R0 << Pa.

Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
a) The equilibrium is unstable. It is obvious from purely mechanical considerations that if the radius of one bubble decreases and the other increases, the pressure in the first bubble (which is inversely proportional to R0) will increase and that in the second bubble will decrease, leading to further changes in respective radii until the system becomes one bubble with radius R1 (see Figure 1.2). The same result can be obtained by considering the free energy of the system.
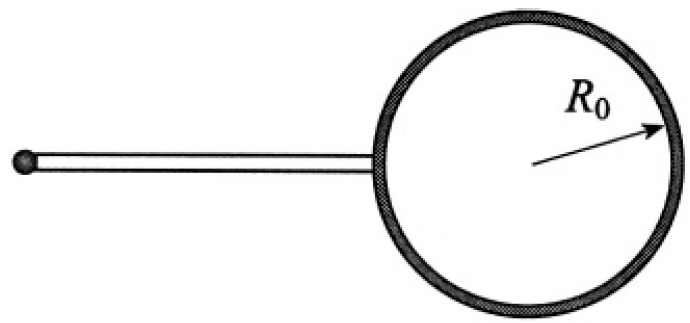
Figure 1.2
b) The free energy of the bubble consists of two parts: a volume part, which is just the free energy of a gas, and a surface part, which is associated with the surface tension:
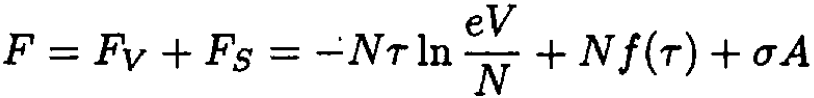 (1)
(1)
The Gibbs free energy
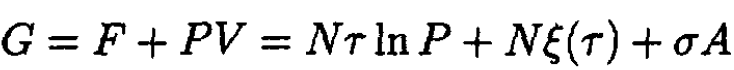 (2)
(2)
The entropy change
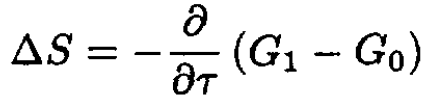
where G1 is the potential of the system with one bubble and G0 is the potential of the initial configuration. We then find
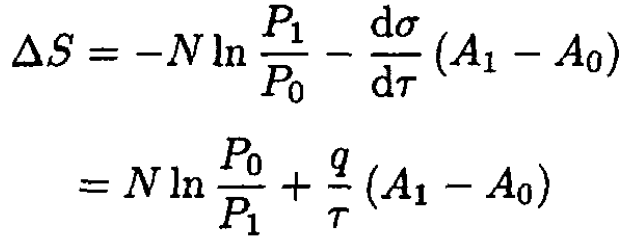 (3)
(3)
where we used the fact that the number of particles did not change and q is the heat necessary to produce a unit area of the film:

So
 (4)
(4)
We can eliminate R1 from the final result by using the following equations:
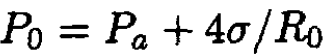 (5)
(5)
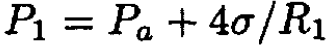 (6)
(6)
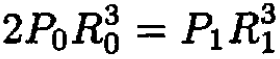 (7)
(7)
where the last equation represents the ideal gas law at constant temperature. This yields the equation
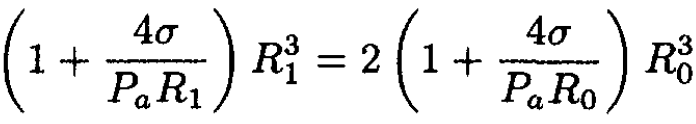 (8)
(8)
Solving this cubic equation in the small σ limit gives
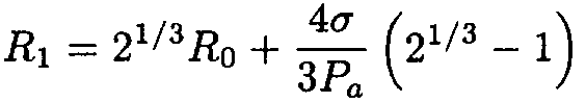 (9)
(9)
Substituting (9) into (4) yields (in the same approximation)
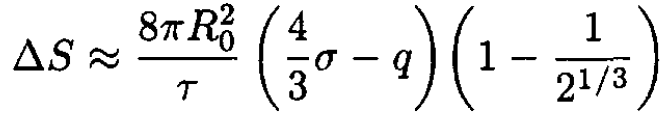 (10)
(10)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


