
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Heat Extraction
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 16
29-8-2016
1657
Heat Extraction
a) A body of mass M has a temperature-independent specific heat C. If the body is heated reversibly from a temperature Ti to a temperature Tf, what is the change in its entropy?
b) Two such bodies are initially at temperatures of 100 K and 400 K. A reversible engine is used to extract heat with the hotter body as a source and the cooler body as a sink. What is the maximum amount of heat that can be extracted in units of MC?
c) The specific heat of water is C = 4.2 J/g K, and its density is 1 g/cm3. Calculate the maximum useful work that can be extracted, using as a source 103 m3 of water at 100°C and a lake of temperature 10°C as a sink.
SOLUTION
a) For a mass of fixed volume we have
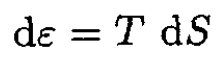 (1)
(1)
So, by the definition of C,
 (2)
(2)
Since C is independent of T, we may rewrite (2) and integrate:
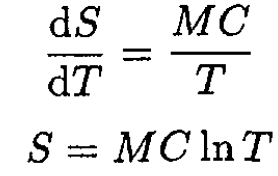 (3)
(3)
The change in entropy is then
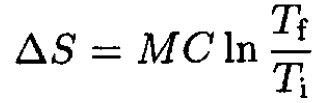 (4)
(4)
b) The maximum heat may be extracted when the entropy remains constant. Equating the initial and final entropies yields the final temperature of the two bodies:
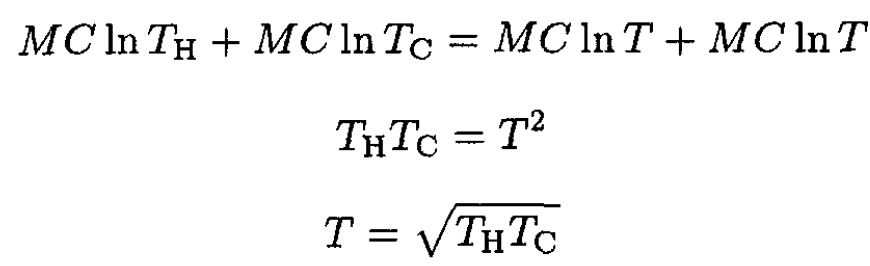 (5)
(5)
The heat extracted, Q, is then equal to the difference in initial and final internal energies of the bodies:
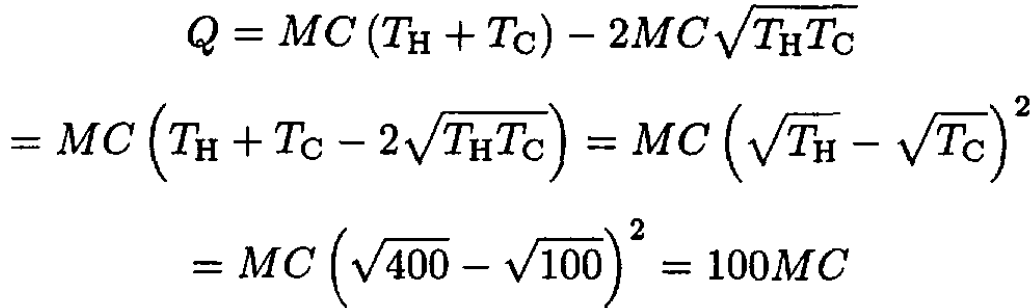 (6)
(6)
c) Here we may calculate the maximum useful work by using the Carnot efficiency of a reversible heat engine operating between two reservoirs, one starting at a high temperature (100°C) and the other fixed (the lake) at 10°C. The efficiency may be written for a small heat transfer as
 (7)
(7)
where the heat dQ transferred from the hot reservoir equals its change in internal energy –MC dT. We may then find the total work by integrating dW as follows:
 (8)
(8)
We may also use the method of part (b) and the fact that the entropy is conserved. Denote the mass of the hot water M and the lake ML. Equating the initial and final entropies gives
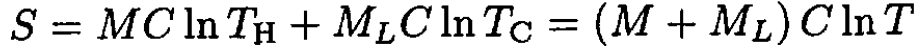 (9)
(9)
Writing the final temperature T as TC + δ, where δ is small (it’s a big lake), and expanding the logarithm, we obtain
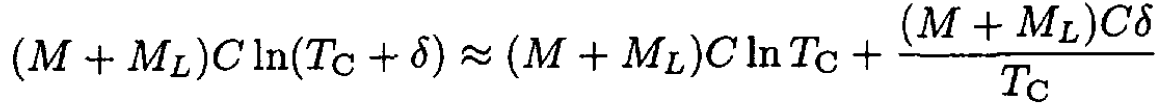 (10)
(10)
Substituting (10) back into (9) gives
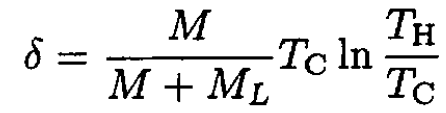 (11)
(11)
As before, the work extracted equals the change in internal energy of the bodies, so
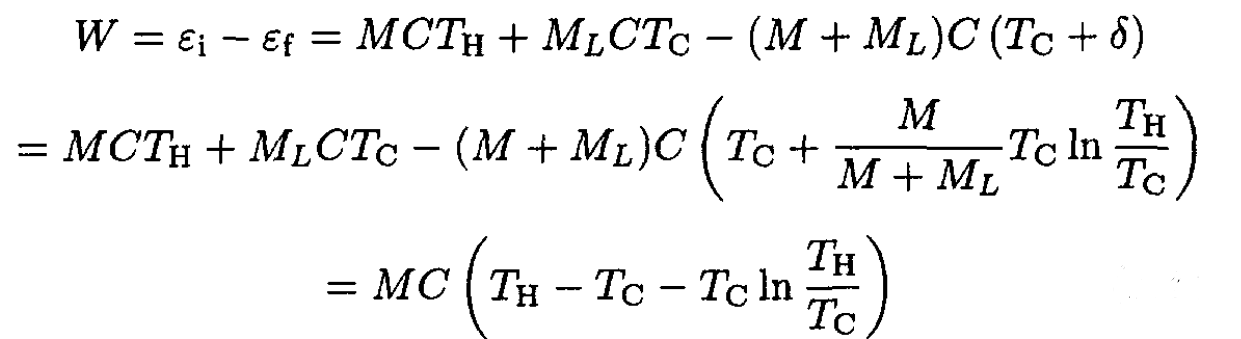
which is the same as above.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















