
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
London Penetration Depth
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 77
9-8-2016
1719
London Penetration Depth
The model used by the brothers F. and H. London suggests that free electrons in a superconductor can be divided into two types: normal, with a density nn, and superconducting, with a density ns (where ns+ nn = n, the density of free electrons). On the surface of the superconductor flows a current with density Js.
a) Using classical arguments, obtain the equation for the electric field E, where
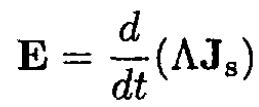 (i)
(i)
where Λ = m/(nse2). Here, m and e are the mass and charge of the electron. Again using classical arguments, write the kinetic energy of superconducting electrons in the form
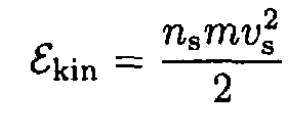
Adding the magnetic field energy, find a minimum of the free energy Fs(h) to obtain a second equation
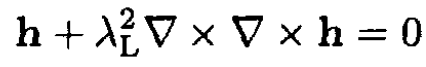 (ii)
(ii)
where h is a microscopic magnetic field inside the superconductor and is the London λL penetration depth.
b) Solve (2) for the boundary between vacuum and a space half filled with superconductor, with an external field H0 parallel to the boundary, and estimate λL (0) for a typical metal superconductor at zero temperature, assuming ns (0) = n.
SOLUTION
a) Equation (i) can be obtained from a naive classical model with a superconducting electron density ns. This derivation is not quite rigorous since we assume spatially uniform fields in the penetration depth. For a unit volume of superconducting electrons in an electric field E,
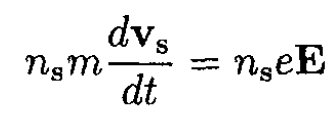 (1)
(1)
The superconducting current density may be written as Js = ns evs. Substituting into (1) gives (i):
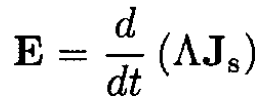
To derive (ii), write the kinetic energy density in the form
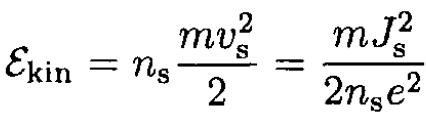
Using Maxwell’s equation
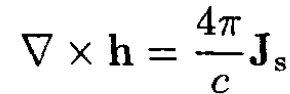
we obtain
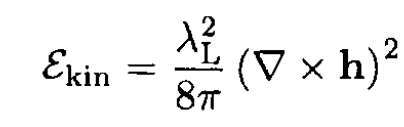 (2)
(2)
where
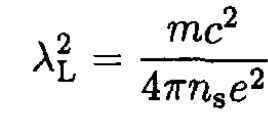 (3)
(3)
Now we can write the free energy in the form
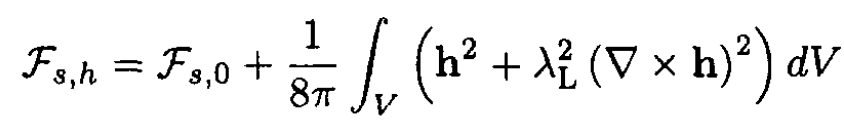
where ∫ h2/(8π)dV accounts for the energy of the magnetic field in the superconductor. We want to find a function h(r) that will minimize the free energy. Note that a more rigorous approach requires that we minimize the Gibbs’ free energy, but the result is the same. Using a standard procedure we take a variation of Fs, h. We can write
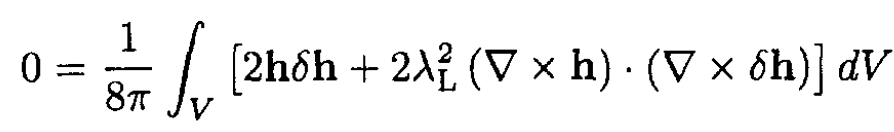 (4)
(4)
The second term in (4) can be transformed using the identity
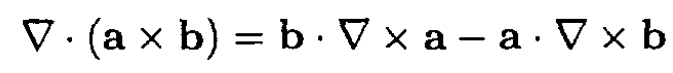
Now we can rewrite (4) in the form
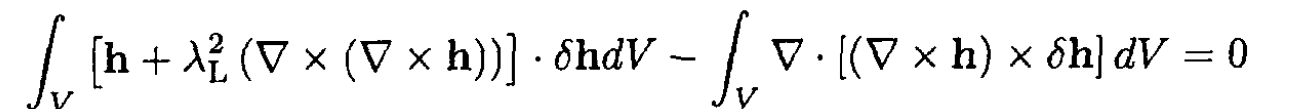 (5)
(5)
The second integral in (5) can be transformed into a surface integral using Gauss’s theorem
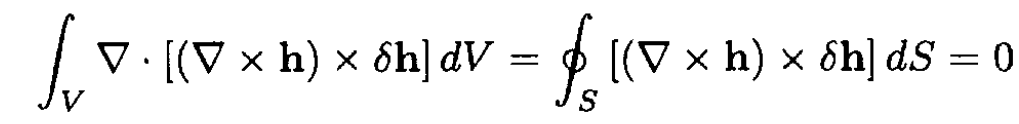
since everywhere on the surface h = H0, and so δh = 0. So, from the first integral in (5), we obtain (ii)

b) Using (ii) and the identity
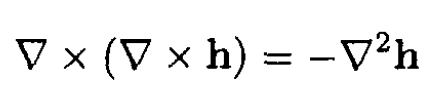
we have
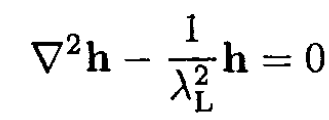
Orient the x direction normal to the boundary and the magnetic field parallel to it, H = H0 ẑ. From the symmetry of the problem, it is obvious that h = h(x) ẑ. Then (ii) becomes
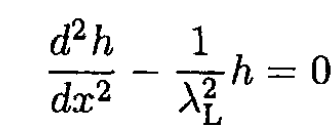
whose solution is
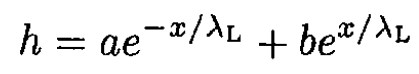
Invoking the boundary conditions h(0) = H0 and h (∞) = 0, we arrive at
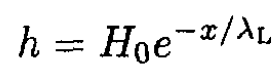
where λL is the London penetration depth introduced in (a) (2). For a typical metal superconductor with one free electron per atom
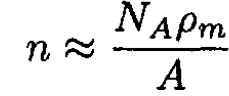
where NA is Avogadro’s number, ρm is the mass density, and A is the atomic mass in grams per mole. For a typical superconductor, n ≈ 1022 – 1023 cm-3. Assuming ns = n at T = 0, we have from (3)
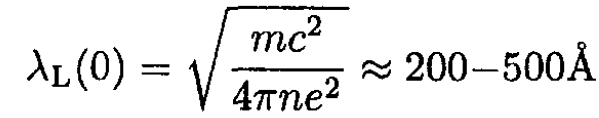
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















