
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Coaxial Cable and Surface Charge
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 54
8-8-2016
1929
Coaxial Cable and Surface Charge
A very long coaxial cable consists of an inner cylinder of radius a and isotropic conductivity σ and a concentric outer cylinder of radius b. The outer shell has infinite conductivity. The space between the cylinders is empty. A uniform, constant current density J, directed along the axial coordinate z, is maintained in the inner cylinder. Return current flows
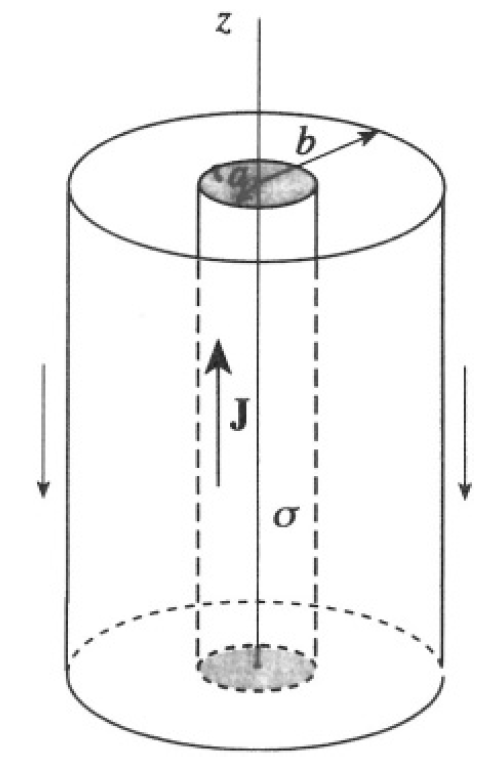
Figure 1.1
uniformly in the outer shell (see Figure 1.1). Compute the surface charge density on the inner cylinder as a function of the axial coordinate z, with the origin z = 0 chosen to be the plane halfway between the two ends of the cable.
SOLUTION
Write down Laplace’s equation in the region between the cylinders in cylindrical coordinates:
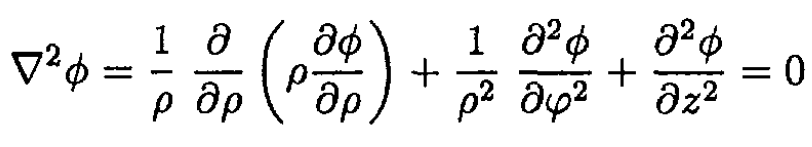
By cylindrical symmetry, ϕ does not depend on φ (see Figure 1.2), so
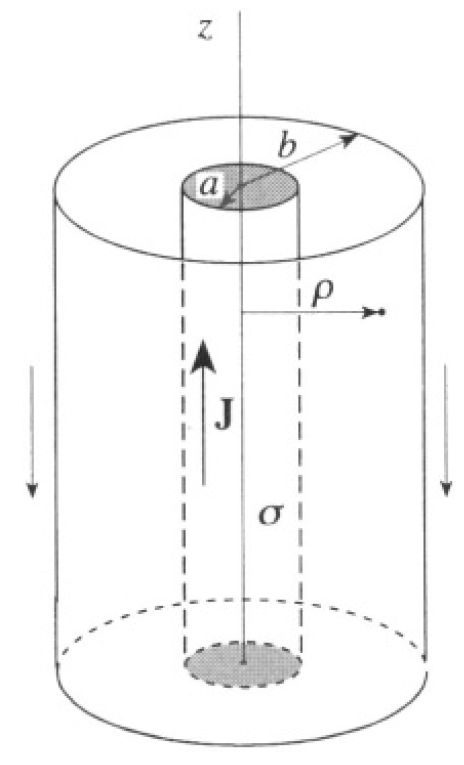
Figure 1.2
Laplace’s equation reduces to
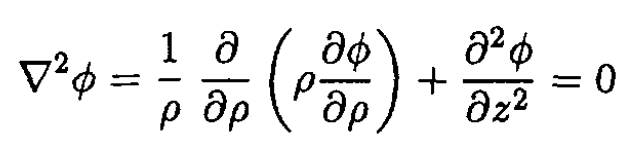 (1)
(1)
As usual, we look for a solution in the form
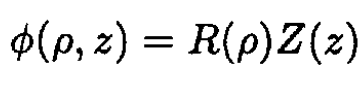
and (1) becomes
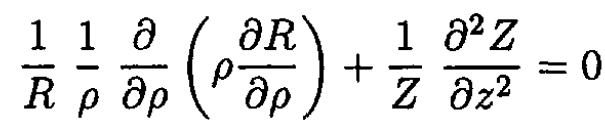 (2)
(2)
From (2), we have
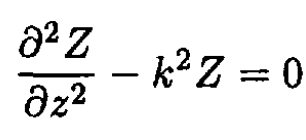 (3)
(3)
where k is a constant. By translational symmetry along the z-axis

so k = 0, and
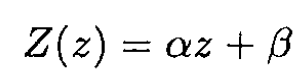
where α and β are constants. The radial part then becomes
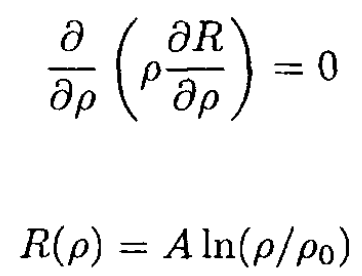 (4)
(4)
So
 (5)
(5)
Imposing the boundary condition that ϕ (ρ, 0) = 0 leads to β = 0, and we have
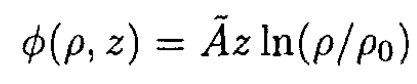 (6)
(6)
where à is a constant (à = αA). We may write the potential differences along the cable as
 (7)
(7)
where we used J = σE, the uniformity of the current density J and isotropic electrical conductivity. We now have
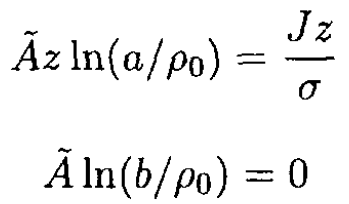 (8)
(8)
From (8), we find
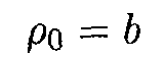 (9)
(9)
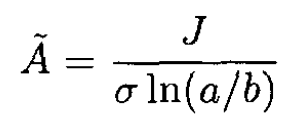 (10)
(10)
For ρ < a, the potential is the same as on the surface, and from (7)and (9)
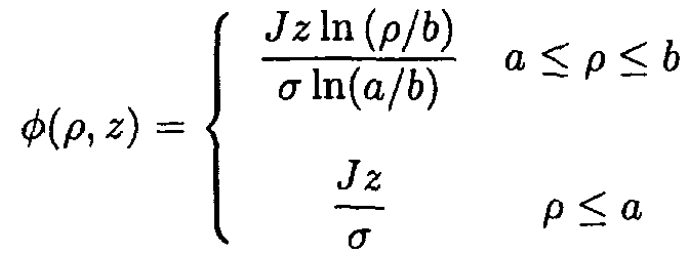
The surface charge density is
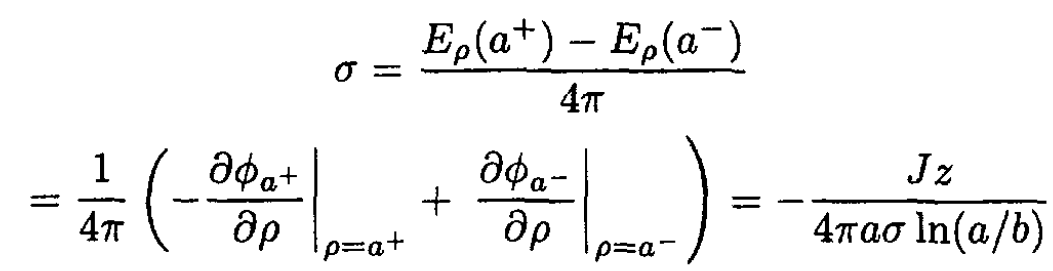
where a+ and a- correspond to the points outside and inside the inner cylinder, respectively.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















