


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-8-2016
Date: 15-3-2021
Date: 11-8-2016
|
Small Particle in Bowl
A small particle of mass m slides without friction on the inside of a hemispherical bowl, of radius R, that has its axis parallel to the gravitational field g. Use the polar angle θ (see Figure 1.1) and the azimuthal angle φ to describe the location of the particle (which is to be treated as a point particle).
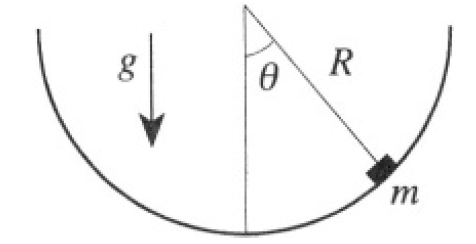
Figure 1.1
a) Write the Lagrangian for the motion.
b) Determine formulas for the generalized momenta and
c) Write the Hamiltonian for the motion.
d) Develop Hamilton's equations for the motion.
e) Combine the equations so as to produce one second order differential equation for as a function of time.
f) If θ = θ0 and θ = 0 independent of time, calculate the velocity (magnitude and direction).
g) If at t = 0, θ = θ0, θ = 0 and φ = 0 calculate the maximum speed at later times.
SOLUTION
a) In spherical coordinates, the Lagrangian
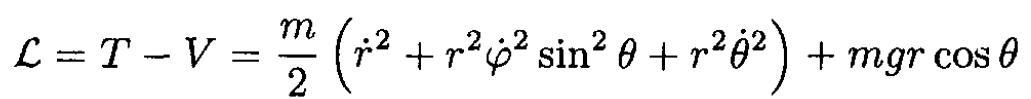
Since we have the restriction r = constant = R (see Figure 1.2),
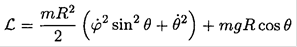 (1)
(1)

Figure 1.2
b) For the generalized momenta
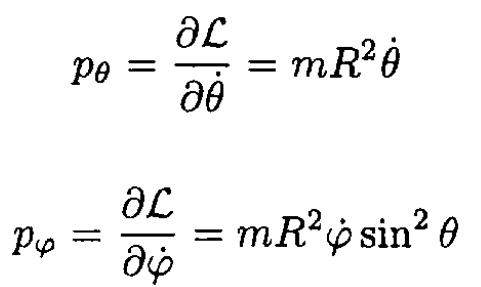 (2)
(2)
c) Find the Hamiltonian of the motion H (p, q, t)
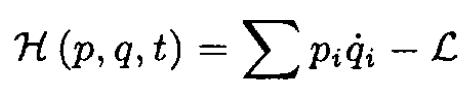
From (b)
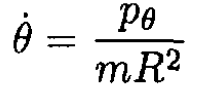 (3)
(3)
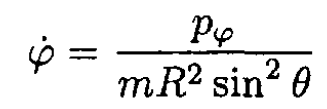 (4)
(4)
The Hamiltonian then becomes
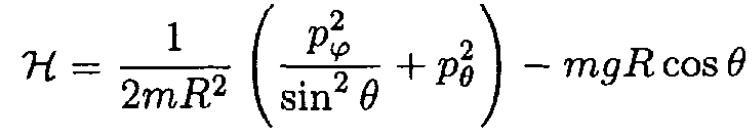 (5)
(5)
d) Let us write Hamilton’s equations
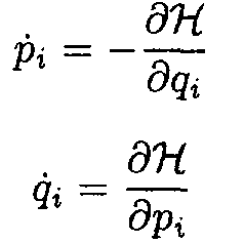
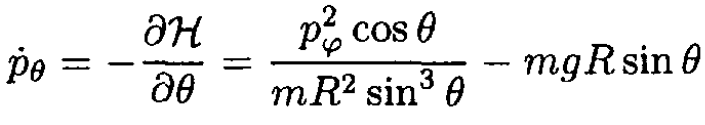 (6)
(6)
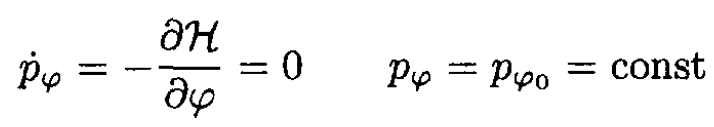 (7)
(7)
e) Differentiate (3) and use (6) and (7)
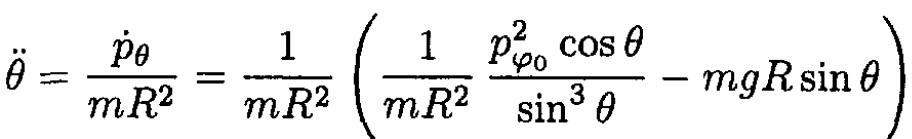 (8)
(8)
f) If θ = θ0, 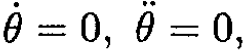 we have
we have
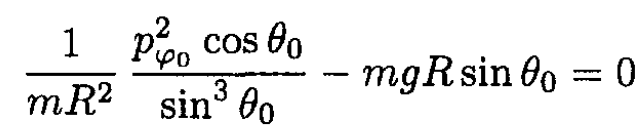 (9)
(9)
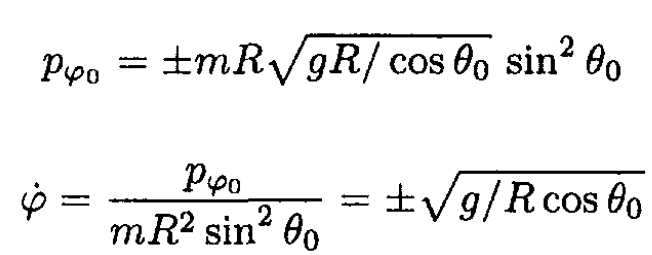 (10)
(10)
Here, the particle slides in a circle at a fixed height in the bowl. The different signs correspond to clockwise or counterclockwise motion.
g) If  at t = 0, then we always have
at t = 0, then we always have
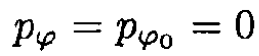
and so
 (11)
(11)
(the equation for a simple pendulum). The energy is conserved and therefore
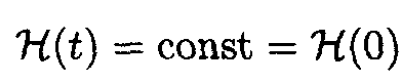 (12)
(12)
Using (2), (5), and (12), we have
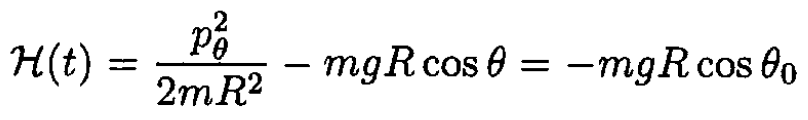
and
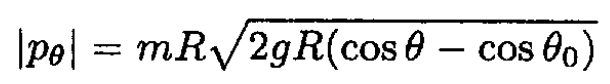
The maximum velocity corresponds to the maximum |pθ| which occurs at θ = 0
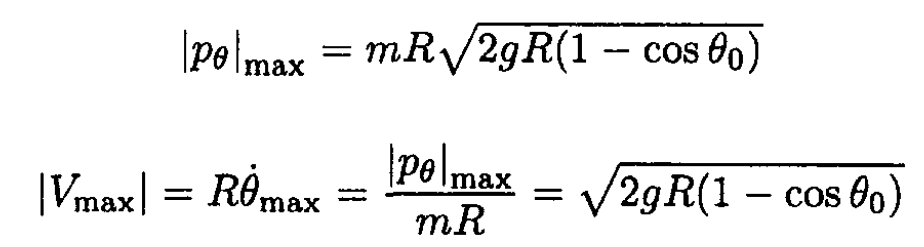
Of course, this result can be obtained much more easily from (11) using elementary methods.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|