
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Adiabatic Invariants
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 31
25-7-2016
1523
Adiabatic Invariants
a) (Adiabatic Invariants) Consider a system with canonical variables
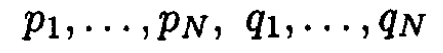
At the time t = 0 let C0 be an arbitrary closed path in phase space and
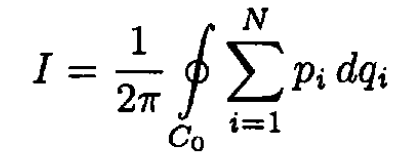
Assume that the point p, q of C0 moves in phase space according to Hamilton's equations. At a later time the curve C0 will have become another closed curve Ct. Show that
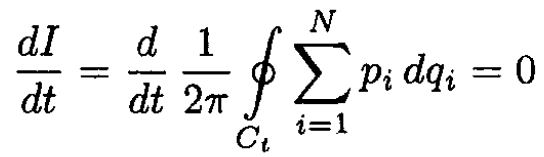
and, for a harmonic oscillator with Hamiltonian H = (p2/2m) + (mω2q2/2) show that
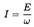
along a closed curve H = (p, q) = E.
b) (Dissolving Spring) A mass m slides on a horizontal frictionless track. It is connected to a spring fastened to a wall. Initially, the amplitude of the oscillations is A1 and the spring constant of the spring is K1. The spring constant then decreases adiabatically at a constant rate until the value K2 is reached. (For instance, assume that the spring is being dissolved in acid.) What is the new amplitude?
Hint: Use the result of (a).
SOLUTION
a)
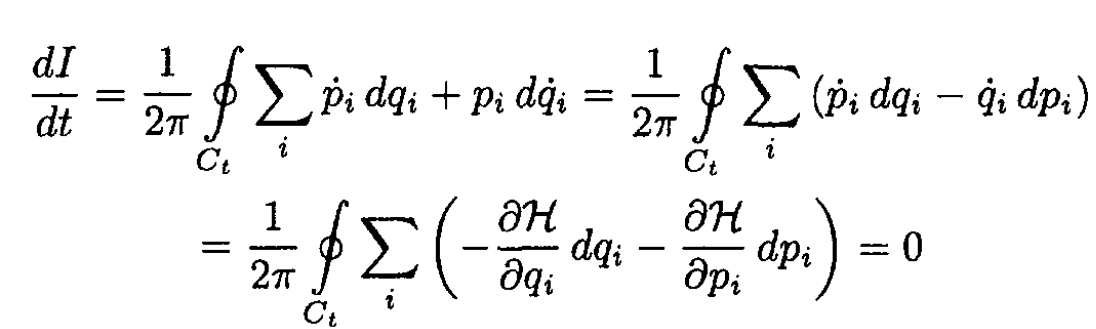
For a harmonic oscillator H(p, q) = E
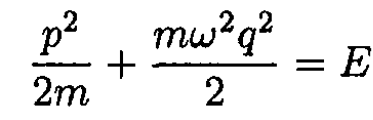
This trajectory in phase space is obviously an ellipse:
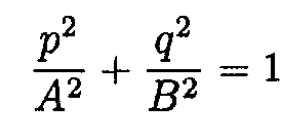
With
 (1)
(1)
The adiabatic invariant

where we transformed the first integral along the curve into phase area integral which is simply I = σ/2π, where σ is the area of an ellipse σ = πAB So, taking A and B from (1) gives

b) The fact that the spring constant decreases adiabatically implies that although the energy is not conserved its rate of change will be proportional to the rate of change in the spring constant: It can be shown that in this approximation the quantity found in (a)—the so-called adiabatic invariant—remains constant. Our spring is of course a harmonic oscillator with frequency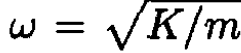 and energy E = (1/2)KA2 So we have
and energy E = (1/2)KA2 So we have
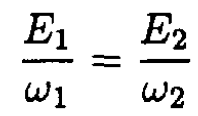 (2)
(2)
or

So from (2), the new amplitude is

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















