


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 25-3-2016
Date: 28-1-2022
Date: 14-8-2019
|
Cis–Trans Isomerism in Alkenes
We knew that the carbon–carbon double bond can be described in two ways. In valence bond language the carbons are sp2-hybridized and have three equivalent hybrid orbitals that lie in a plane at angles of 120° to one another. The carbons form a σ bond by a head-on overlap of sp2 orbitals and form a π bond by sideways overlap of unhybridized π orbitals oriented perpendicular to the sp2 plane, as shown in Figure 1.1
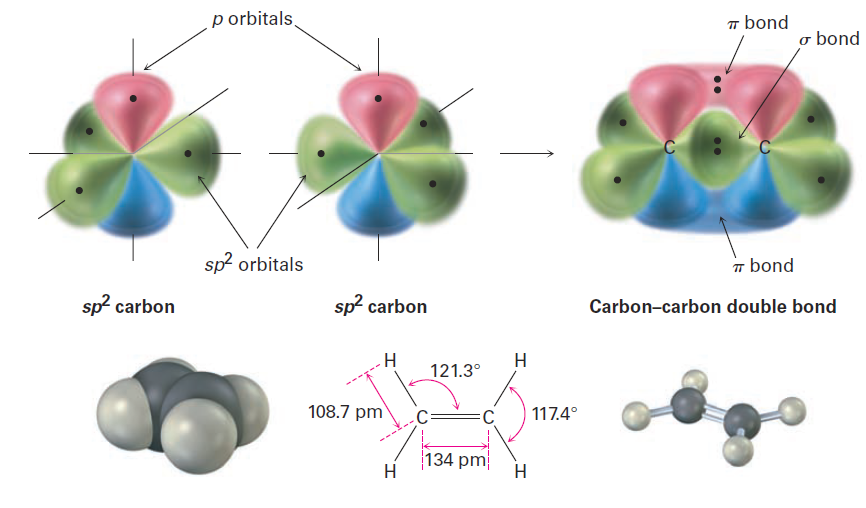
Figure 1.1
In molecular orbital language, interaction between the p orbitals leads to one bonding and one antibonding π molecular orbital. The π bonding MO has no node between nuclei and results from a combination of p orbital lobes with the same algebraic sign. The π antibonding MO has a node between nuclei and results from a combination of lobes with different algebraic signs, as shown in Figure 1.2
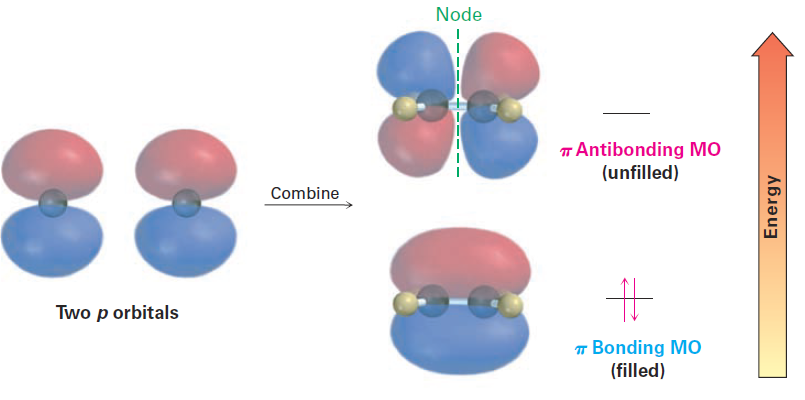
Figure 1.2
Although essentially free rotation around single bonds is possible , the same is not true of double bonds. For rotation to occur around a double bond, the p bond must break and re-form (Figure 1-3). Thus, the barrier to double-bond rotation must be at least as great as the strength of the π bond itself, an estimated 350 kJ/mol (84 kcal/mol). Recall that the barrier to bond rotation in ethane is only 12 kJ/mol.

Figure 1-3: The π bond must break for rotation to take place around a carbon–carbon double bond.
The lack of rotation around carbon–carbon double bonds is of more than just theoretical interest; it also has chemical consequences. Imagine the situation for a disubstituted alkene such as 2-butene. (Disubstituted means that two substituents other than hydrogen are bonded to the double-bond carbons.) The two methyl groups in 2-butene can either be on the same side of the double bond or on opposite sides, a situation similar to that in disubstituted cycloalkanes.
Since bond rotation can’t occur, the two 2-butenes can’t spontaneously interconvert; they are different, isolable compounds. As with disubstituted cycloalkanes, we call such compounds cis–trans stereoisomers. The compound with substituents on the same side of the double bond is called cis- 2-butene, and the isomer with substituents on opposite sides is trans-2-butene (Figure 1-4).
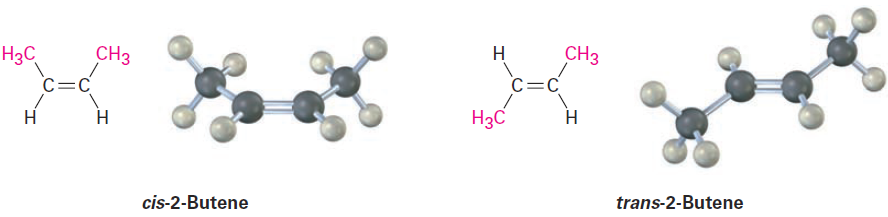
Figure 1-4 Cis and trans isomers of 2-butene. The cis isomer has the two methyl groups on the same side of the double bond, and the trans isomer has methyl groups on opposite sides.
Cis–trans isomerism is not limited to disubstituted alkenes. It can occur whenever both double-bond carbons are attached to two different groups. If one of the double-bond carbons is attached to two identical groups, however, cis–trans isomerism is not possible (Figure 1-5).

Figure 1-5 The requirement for cis–trans isomerism in alkenes. Compounds that have one of their carbons bonded to two identical groups can’t exist as cis–trans isomers. Only when both carbons are bonded to two different groups is cis–trans isomerism possible.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|