


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 29-5-2021
Date: 4-11-2020
Date: 25-4-2016
|
EF-Hand Motif
The majority of calcium-binding proteins involved in intracellular Ca2+ signal transduction are characterized by a common helix–loop–helix structural protein motif in their Ca2+-binding sites that is termed the EF-hand. Well over a thousand EF-hand motif sequences have been identified. An exquisite fine-tuning of the packaging of EF-hands provides these proteins with both high selectivity for Ca2+ and the ability to respond rapidly and efficiently to the modest (100-fold) changes in concentration associated with Ca2+ signals. In fact, the unique relationship between the EF-hand motif and Ca2+ binding extends beyond the ability to transduce Ca2+ signals, as other members of this protein family have critical roles in the uptake, transport and homeostasis of Ca2. +
The term “EF-hand motif” was introduced by Kretsinger on examination of the three-dimensional structure of parvalbumin, the first member of the EF-hand Ca2+-binding protein family whose three-dimensional structure was determined (1). A great deal of structural insight into the variability of the EF-hand motif has been obtained from subsequent X-ray crystallography and NMR solution structure analysis of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins. EF-hand motifs almost always occur in pairs packed together in a face-to-face manner, forming a stable globular domain (Fig. 1). The pairing of sites is presumed to stabilize the protein conformation, increase the Ca2+ affinity of each site over that of isolated sites, and provide a ready means for the cooperativity in the binding of Ca2+ that is critical to their function. The conformations of EF-hands are variable and are dependent on whether ions are bound.
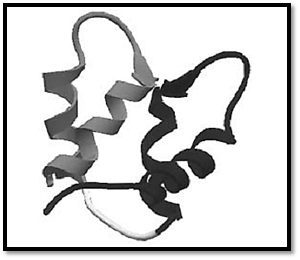
Figure 1. Ribbon diagram of the canonical EF-hand of the N-terminal domain of calmodulin using the coordinates of 1CFC (3).
The canonical EF-hand consists of a 29-residue contiguous segment of polypeptide chain containing an a-helix designated as E in the original parvalbumin structure (residues 1–10), a loop around the calcium ion (residues 10–21), and a second a-helix designated F (residues 19–29). The consensus sequence is shown in Figure 2. Residues 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, and 21 chelate the Ca2+ ion. Residues 10, 12, and 14 provide monodentate oxygen ligands, and residue 21 provides a bidentate oxygen ligand, all via side-chain carboxyl groups. Residue 16 directly coordinates Ca2+ via its main-chain oxygen. Residue 18 ligates Ca2+ indirectly, through a stably bound water molecule. Other residues have been assigned specific roles in stabilizing the EF-hand motif. For example, a central hydrophobic core is formed from the side chains of residues 2, 5, 6, and 9 of helix E; 22, 25, 26, and 29 of helix F; and 17 from the binding loop.
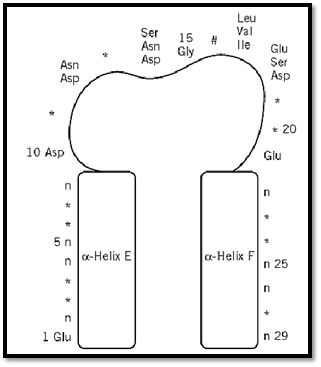
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the consensus sequence for the EF-hand Ca2+-binding motif. Residues marked with * have no constraints on which amino acids occur there. Residue 16, #, chelates the calcium by its backbone carbonyl oxygen atom. The residues of the E and F helices marked “n” must be nonpolar for packing of the two helices.
Most EF-hand proteins use this canonical motif. The S100 proteins (an important subfamily of Ca2+-binding proteins), however, have a two-residue insertion and a modified coordination scheme in the first binding loop. In these pseudo-EF-hands, residues 10, 13, 15, and 18 chelate the Ca2+ ion via their main-chain carbonyl oxygen atoms, whereas residue 20 chelates indirectly via a water molecule, and acidic residue 23 provides bidentate ligation via its side-chain carboxylate. The role of these pseudo-EF-hands in modulating the structure or function of S100 proteins is still under investigation, although there is evidence that the packaging of a pseudo-EF-hand and a canonical EF-hand attenuates the changes in the structure and dynamics of the protein induced by the binding of calcium (2).
References
1. R. H. Kretsinger and C. E. Nockolds (1973) J. Biol. Chem. 248, 3313–3326.
2. N. J. Skelton, J. Kördel, M. Akke, S. Forsén, and W. J. Chazin (1994) Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 239-245.
3. H. Kuboniwa, N. Tjandra, S. Grzesiek, H. Ren, C. B. Klee, and A. Bax (1995) Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 768–776.
4. N. C. J. Strynadka and M. N. G. James (1989) Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58, 951–998.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|