


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 24-3-2016
Date: 25-3-2016
Date: 24-3-2016
|
OPTICS AND CAVITIES
In the IR band where the CO2 laser operates, there are few materials that can be used for cavity optics. For reflectors, a glass substrate over coated with a thin film of copper or gold may be used. This is the most inexpensive option, but these films do absorb a tiny fraction of cavity radiation, heating the glass substrate underneath, so their use is limited to low-powered (usually under 20 W) lasers. Higher-powered lasers generally use solid metal mirrors (in most cases with a film of copper or gold on base metal) or a mirror of solid silicon or molybdenum (both of which reflect well in the IR). The advantage of solid metal mirrors or mirror substrates is that they have excellent thermal dissipation; in many cases, they may be water cooled, allowing even higher-power use.
For an OC one cannot simply use dielectric-coated glass since the glass substrate itself would absorb 10.6-μm radiation, resulting in its destruction. A material transparent to IR is required. Three common materials are germanium, gallium arsenide, and zinc selenide. Germanium is the least expensive but has the highest absorption of the three materials, so its use is limited primarily to lasers of under 100 W. Even then, it is often water cooled since it has a low damage threshold temperature. Gallium arsenide has lower absorption (about two-thirds that of germanium) and can better handle thermal stresses. Zinc selenide has a very low absorption (only 15%that of germanium) and is yellow in color, allowing visible light to pass through it. This feature allows the use of a coaxial HeNe alignment beam, so for higher powered lasers it is the OC material of choice. Note that all three materials have high indexes of refraction, so the interface between these materials and air results in a large reflection. To suppress this, an antireflective coating is required on all optics. The same is true for focusing lenses used for the output beam antireflection coatings are required.
Where a laser uses external optics and a window is required, sodium chloride (salt) may be used. However, this material is hygroscopic; that is, it absorbs water from the atmosphere. Better choices for windows include zinc–selenide. Where a window is employed, it is frequently mounted on metal bellows so that it may purposely be misaligned from the laser tube axis, to prevent feedback from the window surfaces and not the cavity optics. A bellows mount suitable for either windows or mirrors is shown in Figure 1.1. The plasma tube is attached to the rear circular plate, which is bridged to the front plate, with the metal bellows forming gastight
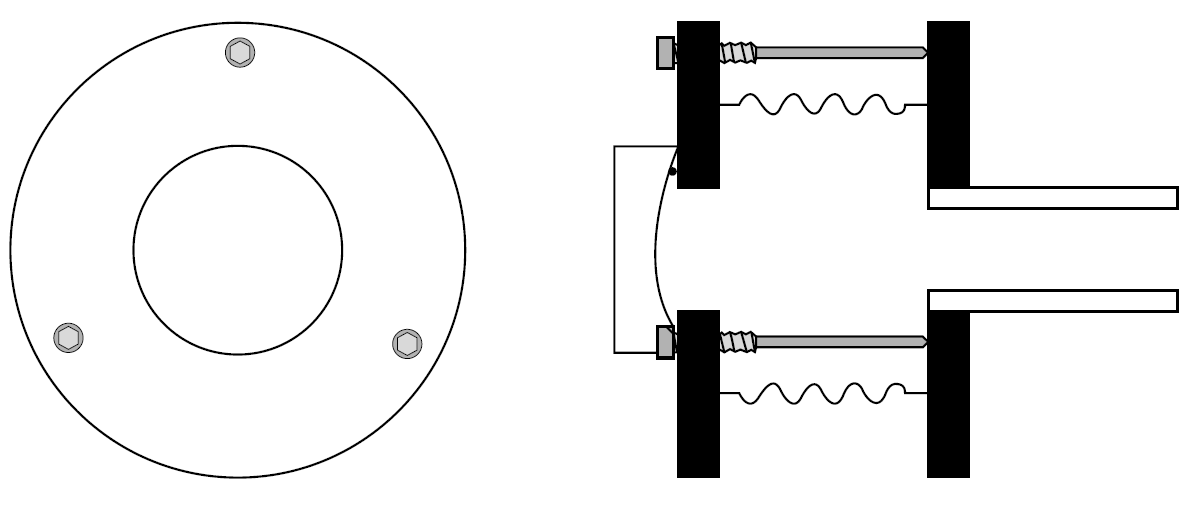
Figure 1.1. Bellows mount for optics.
seals. Adjustment screws between the two plates allow angular adjustment of the optic with respect to the axis of the laser tube.
A variety of cavity configurations may be used in this type of laser, but the most popular (a trade-off between utilization of lasing volume and ease of alignment) is the spherical-plane configuration, often utilizing a spherical mirror of much longer radius than the cavity length. Extremely high powered lasers often use an unstable resonator consisting of two solid metal water-cooled mirrors, with the resulting beam shaped like a donut. At extremely high powers, solid metal mirrors are the only reflectors capable of tolerating the large powers involved. Aside from mirrors, the other problem that arises with extremely high powered lasers is absorption by windows, which will shatter given the huge energies involved: If a window absorbs 1% of an exiting 100-W beam, only 1 W of heat needs to be dissipated, but if 1% of a 10-kW beam is absorbed, that represents 100 W of heat! In these cases aerodynamic windows may be employed, which are simply an open hole in the laser cavity. By passing a fast flow of gas across the face of the hole, contaminants can be prevented from entering the tube.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|