


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية| Plate count method APHA 2001 for aerobic psychrotrophic bacteria in foods |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 2-3-2016
Date: 18-3-2016
Date: 13-3-2016
|
Plate count method APHA 2001 for aerobic psychrotrophic bacteria in foods
Method of the American Public Health Association (APHA), as described in the 4th Edition of the Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods (Cousin et al., 2001) and the 17th Edition of the Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products (Frank and Yousef, 2004).
The Compendium recommends that the samples intended to be analyzed for the enumeration of aerobic psychrotrophics be analyzed within a 6h interval, counting from the moment the sample was collected. Cold storage does not inhibit their multiplication and the generation time of several of these microorganism falls within this time interval. Freezing is not recommended for these samples, since it can cause injuries to or the death of several microorganisms. If freezing is considered indispensable, it must be taken into account when evaluating the results that part of the microbiota may have been lost.
1- Material required for analysis
Preparation of the sample and serial dilutions
• Diluent: 0.1% Peptone Water (PW) or Butterfield’s Phosphate Buffer
• Dilution tubes containing 9 ml 0.1% Peptone Water (PW) or Butterfield’s Phosphate Buffer
• Observation: to check on special cases in which either the type or volume of diluent vary as a function of the sample to be examined. Spread plate count
• Culture media: Plate Count Agar (PCA) which can be substituted for Trypticase Soy Agar (TSA) or Petrifilm™ Aerobic Count plates (3M Microbiology Products)
• Laboratory incubator set to 7 ± 1°C
• Laboratory incubator set to 17 ± 1°C (optional)
2- Procedure
A general flowchart for enumeration of aerobic psychrotrophic bacteria in foods using the plate count method APHA 2001 is shown in Figure 1Follow the same procedure as described for total aerobic mesophilic counts, changing only the incubation condition(s).
Pour plate is not recommended because these bacteria are heat-sensitive and may be affected by the hot or warm culture medium. Incubation can be done at 7 ± 1°C for 10 days or 17 ± 1°C for 16h, followed by 3 more days at 7 ± 1°C. The Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products (Frank and Yousef, 2004) recommends, for milk and dairy products, pour plate using PCA cooled to 45 ± 1°C, before pouring the culture medium over the inoculum. Incubate at 7 ± 1°C for 10 days.
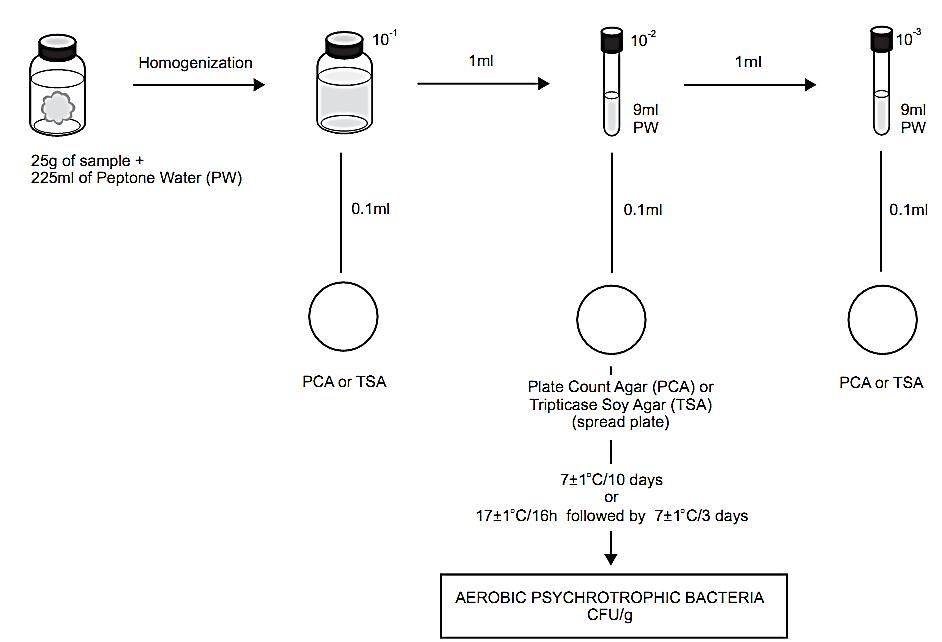
Figure 1 Scheme of analysis for enumeration of aerobic psychrotrophic bacteria in foods using the plate count method APHA 2001 (Cousin et al., 2001).
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
Cousin, M.A., Jay, J.M. & Vasavada, P.C. (2001) Psychrotrophic micro-rganisms. In: Downes, F.P. & Ito, K. (eds). Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods. 4th edition. Washington, American Public Health Association. Chapter 13, pp. 159–166.
Frank, J.F. & Yousef, A.E. (2004) Tests for groups of microrganisms. In: Wehr, H.M. & Frank, J.F (eds). Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products. 17th edition. Washington, Ameri-can Public Health Association. Chapter 8, pp. 227–248.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة الحسينية تطلق فعاليات المخيم القرآني الثالث في جامعة البصرة
|
|
|