


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 28-2-2016
Date: 24-2-2016
Date: 12-7-2020
|
Atmospheric “Windows”
Earth’s atmosphere presents an opaque barrier to much of the electromagnetic spectrum. The atmosphere absorbs most of the wavelengths shorter than ultraviolet, most of the wavelengths between infrared and microwaves, and most of the longest radio waves. That leaves only visible light, some ultraviolet and infrared, and short wave radio to penetrate the atmosphere and bring information about the universe to our Earth-bound eyes and instruments.
The main frequency ranges allowed to pass through the atmosphere are referred to as the radio window and the optical window. The radio window is the range of frequencies from about 5 MHz to over 300 GHz (wavelengths of almost 100 m down to about 1 mm). The low-frequency end of the window is limited by signal absorption in the ionosphere, while the upper limit is determined by signal attenuation caused by water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Atmospheric Windows to Electromagnetic Radiation
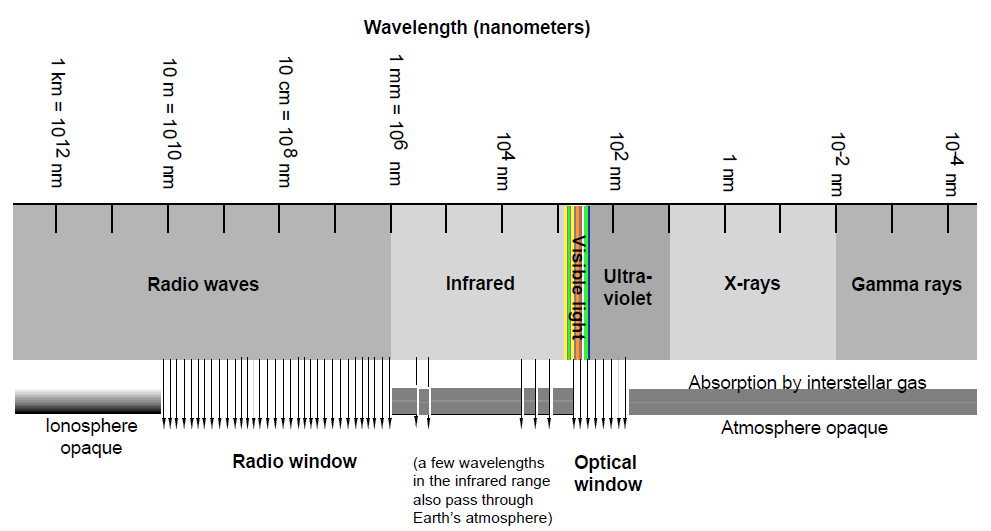
The optical window, and thus optical astronomy, can be severely limited by atmospheric conditions such as clouds and air pollution, as well as by interference from artificial light and the literally blinding interference from the sun’s light. Radio astronomy is not hampered by most of these conditions. For one thing, it can proceed even in broad daylight. However, at the higher frequencies in the atmospheric radio window, clouds and rain can cause signal attenuation. For this reason, radio telescopes used for studying sub-millimeter wavelengths are built on the highest mountains, where the atmosphere has had the least chance for attenuation. (Conversely, most radio telescopes are built in low places to alleviate problems with human-generated interference).



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جمعية العميد تناقش التحضيرات النهائية لمؤتمر العميد الدولي السابع
|
|
|