


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-07-31
Date: 2023-11-13
Date: 19-5-2022
|
Bristol l
Intrusive r occurs in part because loan words ending in unstressed final -a (e.g. India, banana) had no counterparts in English when they entered the language. Speakers therefore assimilated them to something similar, in most cases the final -er lexical set (e.g. reader, carer), for which /r/ is deleted in non-rhotic areas except before a vowel. In Bristol, a rhotic city in the west of England, these words were assimilated not to the -er set but to the -le set (e.g. little, apple), with the result that banana is pronounced ‘bananal’ and pairs such as idea/ideal and area/aerial are homophonous.
Because Bristol is so out of step with other English regions in this regard, Bristol l has become widely ridiculed outside the city and is increasingly avoided by all but lowest-status Bristolians as a consequence. An accent feature that is so salient as to attract mockery is called a stereotype.
In similar vein, an appeal to underlying representations can illuminate some otherwise puzzling phenomena in Standard French, where many words have an orthographical final e which is not pronounced (‘mute e’):

Similarly, many words end in orthographical consonants that are not realized: trop, les, bon. It is not uncommon for pronunciation and spelling to be out of step, but in this case standard French orthography may reflect some important facts about French phonology. In spite of the fact that ‘mute e’ is not pronounced, many phonologists would suggest that vase is underlyingly 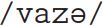 , and trop underlyingly
, and trop underlyingly 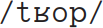 , with a deletion rule being applied to delete the final segment in each case.
, with a deletion rule being applied to delete the final segment in each case.
Once more, a seemingly counter-intuitive approach captures a number of important generalizations. Firstly, we know that the final mute -e is an orthographic holdover from a time when word-final schwa was pronounced: 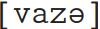 was once the normal pronunciation, and remains so in many parts of southern France today. So, rather like our earlier /r/ example from English, our underlying representation captures a synchronic fact about French and a diachronic one. Secondly, even for speakers who don’t normally pronounce the final schwa, there are occasions when this consonant reappears, typically to break up sequences of three consonants, so Jacques est le maître
was once the normal pronunciation, and remains so in many parts of southern France today. So, rather like our earlier /r/ example from English, our underlying representation captures a synchronic fact about French and a diachronic one. Secondly, even for speakers who don’t normally pronounce the final schwa, there are occasions when this consonant reappears, typically to break up sequences of three consonants, so Jacques est le maître 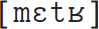 but Maître Jacques
but Maître Jacques  .
.
Similarly, many words have latent word-final consonants which appear before a vowel in what is known as liaison, thus les gens 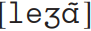 ‘people’ but les amis ‘friends’
‘people’ but les amis ‘friends’  . But why is the final consonant deleted in some cases, but not in others? One answer would be that the final [z] of vase is always pronounced because in its abstract representation it is non-final, and the underlying final schwa ‘blocks’ the deletion rule. The abstraction is arguably therefore a price worth paying for a richer analysis of what French speakers ‘know’ about their language, namely that some word-final consonants are always pronounced, but others are only pronounced in certain environments.
. But why is the final consonant deleted in some cases, but not in others? One answer would be that the final [z] of vase is always pronounced because in its abstract representation it is non-final, and the underlying final schwa ‘blocks’ the deletion rule. The abstraction is arguably therefore a price worth paying for a richer analysis of what French speakers ‘know’ about their language, namely that some word-final consonants are always pronounced, but others are only pronounced in certain environments.
|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
خدمات متعددة يقدمها قسم الشؤون الخدمية للزائرين
|
|
|