


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 20-10-2015
Date: 18-10-2015
Date: 20-10-2015
|
Born: about 250 BC in Caunus, Caria, Asia Minor (now in Turkey)
Died: about 190 BC
There is certainly more than one mathematician called Dionysodorus and this does make it a little difficult in deciding exactly what was studied by each. Strabo, the Greek geographer and historian (about 64 BC - about 24 AD), describes a mathematician named Dionysodorus who was born in Amisene, Pontus in northeastern Anatolia on the Black Sea.
The Dionysodorus we are interested in here is the mathematician Dionysodorus who Eutocius states solved the problem of the cubic equation using the intersection of a parabola and a hyperbola. This was related to a problem of Archimedes given in On the Sphere and Cylinder. It was thought until early this century that the Dionysodorus who Eutocius refers to was Dionysodorus of Amisene described by Strabo.
There is a second Dionysodorus who appears in the writings of Pliny. In Natural history Pliny mentions a certain Dionysodorus who measured the earth's radius and gave the value 42000 stades. Strabo distinguishes this Dionysodorus from Dionysodorus of Amisene and it is now thought that the Dionysodorus referred to by Pliny is not the mathematician who solved the problem of the cubic equation. Interestingly Pliny died as a result of the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD and it is as a consequence of this eruption that new information regarding a mathematician Dionysodorus was published in 1900.
This new information was found by W Cronert in a papyrus found at Herculaneum. When Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD, Herculaneum together with Pompeii and Stabiae, was destroyed. Herculaneum was buried by a compact mass of material about 16 metres deep which preserved the city until excavations began in the 18th century. Special conditions of humidity of the ground conserved wood, cloth, food, and in particular papyri which give us important information. One papyrus states [3]:-
Philonides was a pupil, first of Eudemus, and afterwards of Dionysodorus, the son of Dionysodorus the Caunian.
Eudemus is Eudemus of Pergamum whom Apollonius dedicated two books of his Conics and, in the introduction to Book II, asks Eudemus to show the book to Philonides. We can date Dionysodorus from this information as just a little younger than Apollonius. There is another interesting comment in the papyrus which states that Philonides published some of the lectures by his teacher Dionysodorus.
Shortly after Cronert published details of the fragments of papyri relating to Dionysodorus which had been found at Herculaneum, Schmidt published a commentary on the material in which he argued convincingly that the Dionysodorus who solved the cubic equation using the intersection of a parabola and a hyperbola was the Dionysodorus of Caunus referred to in the Herculaneum papyrus. Caunus is in Caria and is now in Turkey. It is close to Perga in Pamphylia where Apollonius was born.
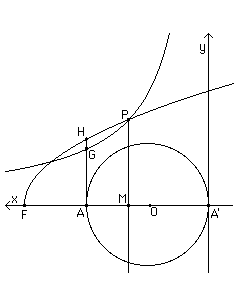 The method which Eutocius describes to cut a sphere in a given ratio, crediting it to Dionysodorus, uses a parabola and a rectangular hyperbola. It is a beautiful construction and in the description that follows we essentially follow the method described by Eutocius (see also [1] and [3]).
The method which Eutocius describes to cut a sphere in a given ratio, crediting it to Dionysodorus, uses a parabola and a rectangular hyperbola. It is a beautiful construction and in the description that follows we essentially follow the method described by Eutocius (see also [1] and [3]).
Let AA' be the diameter of the sphere centre O. We wish to find a plane which divides the sphere in the ratio m : n. Take F on A'A produced so that FA = AO. Let AG be perpendicular to AA' where G is the point with FA : AG = (m+n) : n. Let H be the point on AG withAH2= FA.AG and draw the parabola with vertex at F through H. Draw the rectangular hyperbola through G with the x and y axes as its asymptotes. Let the hyperbola cut the parabola at P and draw PM perpendicular to AA'. Then Dionysodorus proved that the plane through M with AA' as its normal will cut the sphere in the given ratio m : n.
Heron also mentions Dionysodorus as the author of a work On the Tore which, because of the subject matter, must almost certainly be written by the Dionysodorus we are describing here. In this work Dionysodorus calculates the volume of a torus and shows that it is equal to the product of the area of the generating circle with the length of the circle traced by its centre rotating about the axis of revolution. It is clear that Dionysodorus used the methods of Archimedes in proving his result.
Dionysodorus is believed to have invented a conical sundial. The report fails to make it clear which Dionysodorus this is, but the fact that the Dionysodorus described here worked on conic sections makes it likely that he is also the person to have studied a conical sundial. In [2] the likely form that Dionysodorus's sundial would take is discussed. A conjectured reconstruction is given in [1].
Books:
Articles:



|
|
|
|
5 علامات تحذيرية قد تدل على "مشكل خطير" في الكبد
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
لحماية التراث الوطني.. العتبة العباسية تعلن عن ترميم أكثر من 200 وثيقة خلال عام 2024
|
|
|