


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-09-09
Date: 2023-09-29
Date: 2024-01-04
|
Fricative articulations are the result of two articulators being in close approximation with each other. This is a degree of stricture whereby the articulators are held close enough together for air to pass between them, but because the gap between them is small, the airflow becomes turbulent and creates friction noise. (In lay terms, we might talk about a ‘hissing’ sound.) Fricatives in English include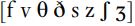 , the sounds represented orthographically by the underlined portion: fish, vow, think, then, loose, lose, wish, vision. Notice that there are not very consistent representations particularly for the sounds
, the sounds represented orthographically by the underlined portion: fish, vow, think, then, loose, lose, wish, vision. Notice that there are not very consistent representations particularly for the sounds 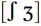 in English spelling.
in English spelling.
Fricative articulations can be held for as long as there is sufficient air to expel. The amount of friction generated depends on the amount of air being forced through the stricture and on the degree of stricture. If you produce a [s] sound and then push more air out, you will notice an increase in the loudness (intensity) of the friction. If you do this and at the same time make the tongue tenser, the intensity of the friction will increase and the friction will sound ‘sharper’. On the other hand, if you relax the articulators in producing a [s] sound, you will notice that the friction gets quieter and that it changes quality, becoming ‘flatter’.
Affricates are plosives which are released into fricatives. English has two of these: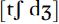 , both postalveolar, as in ‘church’ and ‘judge’.
, both postalveolar, as in ‘church’ and ‘judge’.
The sounds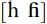 as in ‘heart’ and ‘ahead’ are voiceless and voiced glottal fricatives respectively. These sounds are produced with friction at the glottis.
as in ‘heart’ and ‘ahead’ are voiceless and voiced glottal fricatives respectively. These sounds are produced with friction at the glottis.
Tongue shape plays a determining role in the overall sound of fricatives.
|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|