

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Solvolysis
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
3-1-2022
2594
Solvolysis
Many SNSN reactions are carried out using the solvent as the nucleophilic agent. They are called solvolysis reactions and involve solvents such as water, ethanol, ethanoic acid, and methanoic acid. Two examples are
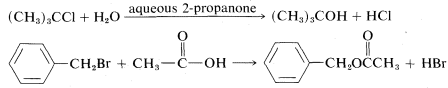
In these examples, solvolysis is necessarily a first-order reaction, because normally the solvent is in such great excess that its concentration does not change appreciably during reaction, and hence its contribution to the rate does not change. However, that the overall rate is first order does not mean the reaction necessarily proceeds by an SN1 mechanism, particularly in solvents such as water, alcohols, or amines, which are reasonably good nucleophilic agents. The solvent can act as the displacing agent in an SN2 reaction.
To distinguish between SN1 and SN2 mechanisms of solvolysis requires other criteria, notably stereochemistry, and the effect of added nucleophiles on the rate and nature of the reaction products. For example, it often is possible to distinguish between SN1SN1 and SN2SN2 solvolysis by adding to the reaction mixture a relatively small concentration of a substance that is expected to be a more powerful nucleophile than the solvent. If the reaction is strictly SN1, the rate at which RX disappears should remain essentially unchanged because it reacts only as fast as R⊕ forms, and the rate of this step is not changed by addition of the nucleophile, even if the nucleophile reacts with R⊕. However, if the reaction is SN2, the rate of disappearance of RX should increase because RX reacts with the nucleophile in an SN2 reaction and now the rate depends on both the nature and the concentration of the nucleophile.
Many organic chemists, and indeed the previous versions of this book, use the term "carbonium ion" for species of this kind. However, there is well-established usage of the -onium suffix, for ammonium, oxonium, chloronium, and so on, to denote positively charged atoms with filled valence shells. In the interest of greater uniformity of nomenclature we shall use "carbocation" for carbon positive ions that have unfilled valence shells (6 electrons).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















