


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 29-3-2021
Date: 11-4-2021
Date: 30-4-2021
|
Resistances in series-parallel
Sets of resistors, all having identical ohmic values, can be connected together in parallel sets of series networks, or in series sets of parallel networks. By doing this, the total power handling capacity of the resistance can be greatly increased over that of a single resistor.
Sometimes, the total resistance of a series-parallel network is the same as the value of any one of the resistors. This is always true if the components are identical, and are in a network called an n-by-n matrix. That means, when n is a whole number, there are n parallel sets of n resistors in series (A of Fig. 1), or else there are n series sets of n resistors in parallel (B of Fig. 1). Either arrangement will give exactly the same results in practice.
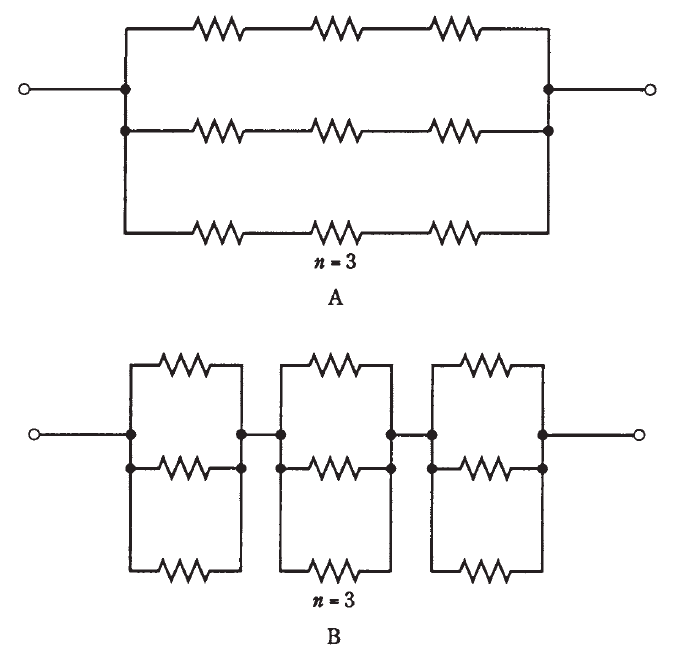
Fig. 1: Series-parallel combinations. At A, sets of series resistors are connected in parallel. At B, sets of parallel resistors are in series.
Engineers and technicians sometimes use this to their advantage to get resistors with large power-handling capacity. Each resistor should have the same rating, say 1 W. Then the combination of n by n resistors will have n2 times that of a single resistor. A 3 × 3 series-parallel matrix of 2-W resistors can handle 32 × 2 = 9 × 2 = 18 W, for example.
A 10×10 array of 1-W resistors can take 100 W. Another way to look at this is to see that the total power-handling capacity is multiplied by the total number of individual resistors in the matrix. But this is only true if all the resistors have the same ohmic values, and the same power-dissipation ratings.
It is unwise to build series-parallel arrays from resistors with different ohmic values or power ratings. If the resistors have values and/or ratings that are even a little nonuniform, one of them might be subjected to more current than it can withstand, and it will burn out. Then the current distribution in the network can change so a second component fails, and then a third. It’s hard to predict the current and power distribution in an array when its resistor values are all different. So it’s hard to know whether
any of the components in such a matrix are going to burn out.
If you need a resistance with a certain power-handling capacity, you must be sure the network can handle at least that much power. If a 50-W rating is required, and a certain combination will handle 75 W, that’s alright. But it isn’t good enough to build a circuit that will handle only 48 W. Some extra tolerance, say 10 percent over the minimum rating needed, is good, but it’s silly to make a 500-W network using far more resistors than necessary, unless that’s the only convenient combination given the parts available.
Nonsymmetrical series-parallel networks, made up from identical resistors, will increase the power-handling capability. But in these cases, the total resistance will not be the same as the value of the single resistors. The overall power-handling capacity will always be multiplied by the total number of resistors, whether the network is symmetrical or not, provided all the resistors are the same. In engineering work, cases sometimes do arise where nonsymmetrical networks fit the need just right.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|