


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-9-2020
Date: 21-9-2020
Date: 21-9-2020
|
Molar Heat Capacity
If, instead of measuring the heat capacity of a unit mass, we measure the heat capacity of a mole of a substance, we call the result the molar heat capacity. For example a water molecule H2O with 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen atom is 18 times as massive as a hydrogen atom. Its molecular weight is 18, and thus a mole of water has a mass of 18 grams. As a result it takes 18 calories to raise the temperature of a mole of water 1 degree centigrade, and thus the molar heat capacity of water is 18 calories/ mole °C or 18 × 4.186 = 75.3 joules/mole °C. For the units, instead of degrees centigrade, we can use kelvins, which are the same size. Thus we can write
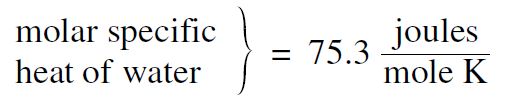 ......(1)
......(1)
as an example of a molar specific heat.
Predicting the specific heat of a substance, even with an understanding of the atomic and molecular processes involved, turned out to be a much more difficult subject than expected. The first time a failure of Newtonian mechanics was detected was during the efforts to predict the specific heats of various gases. This failure was due to quantum mechanics being necessary to fully understand what happened to the added heat energy.
There is one example, however, where the simple picture of atoms we have been discussing gives the correct answer. That is for the specific heat of helium gas. We will discuss that example here, an entire chapter devoted to the subject.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|