
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Newton’s laws of motion
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 170
9-8-2020
1932
Newton’s laws of motion
Kepler’s three laws provide a convenient and highly accurate way of describing the orbits of planets and the way in which the planets pursue such orbits. They do not, however, give any physical reason whatsoever why planetary motions obey these laws. Newton’s three laws of motion, coupled with his law of gravitation, provided the reason. We consider the three laws of motion before looking at the law of gravitation.
Newton’s three laws of motion laid the foundations of the science of dynamics. Though some, if not all of them, were implicit in the scientific thought of his time, his explicit formulation of these laws and exploration of the consequences in conjunction with his law of universal gravitation did more to bring into being our modern scientific age than any of his contemporaries’ work.
They may be stated in the following form
(1) Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniformmotion in a straight line except insofar as it is compelled to change that state by an external impressed force.
In other words, in the absence of any force (including friction), an object will remain stationary or, if moving, will continue to move with the same speed in the same direction forever.
(2) The rate of change of momentum of the body is proportional to the impressed force and takes place in the direction in which the force acts.
Momentum is mass multiplied by velocity. The second law states that the rate at which the momentum changes will depend upon the size of the force acting on the object and naturally enough also depends upon the direction in which the force acts. In calculus, d/dt denotes a rate of change of some quantity.
Both velocity v and force F are directed quantities or vectors, i.e. they define specific directions and such directed quantities are usually underlined or printed in bold type. Mass m is not a directed quantity. We may, therefore, summarize laws (1) and (2) by writing
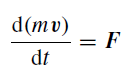 (1)
(1)
where we have chosen the unit of force so that the constant of proportionality is unity. Since in most dynamical problems the mass is constant, we may rewrite equation (1) as
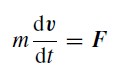 (2)
(2)
or
mass × acceleration = impressed force. (3)
(3) To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
The rocket working in the vacuum of space is an excellent example of this law. The action of ejecting gas at high velocity from the rocket engine in one direction results in the acquiring of velocity by the rocket in the opposite direction (the reaction). It is also found that the momentum given to the gas is equal to the momentum acquired by the rocket in the opposite direction.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















