


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 22-4-2020
Date: 6-4-2020
Date: 4-2-2020
|
Liquid lasers consist of a liquid active material usually composed of an organic dye compound. The most common type of liquid laser uses rhodamine 6G dye mixed with alcohol and is excited by different types of lasers, such as an argon-ion laser or a nitrogen laser. Organic dyes are large compounds that have absorption bands in the UV or visible region with a strong intense fluorescence spectrum. The free π electrons of the dye are excited using an optical pumping source and the transition from the S1 to the S0 state creates the lasing light (see Jablonski diagrams). Liquids are generally used because they can easily be tuned to emit a certain wavelength by changing the resonant frequency within the cavity. Wavelengths from the visible to the infrared can be covered. There are many benefits of liquid lasers, some include that they can be cooled in a relative amount of time, they cannot be damaged unlike a solid-laser, and their production is cost-effective. The efficiency of liquid lasers is low because the lifetime of the excited state is relatively short; there are many non-radiative decay processes, and the material degrades over time. Liquid lasers tend to be used only as a pulse laser when tunability is required. Liquid lasers can be used for high-resolution spectroscopy since they are easily tuned over a wide range of wavelengths. They can also be used because they have concentrations which are manageable when dissolved in solids or other liquids.
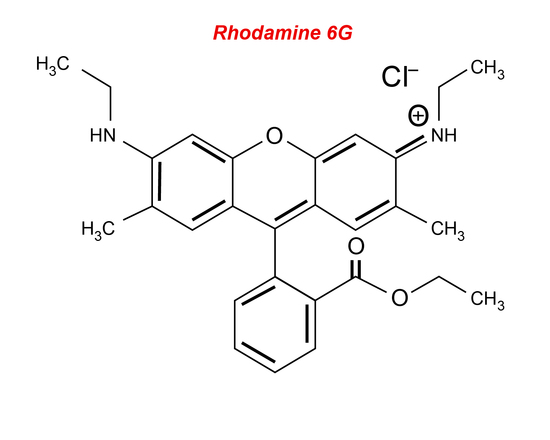
Figure 1. Rhodamine 6G molecule



|
|
|
|
5 علامات تحذيرية قد تدل على "مشكل خطير" في الكبد
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
لحماية التراث الوطني.. العتبة العباسية تعلن عن ترميم أكثر من 200 وثيقة خلال عام 2024
|
|
|