


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-7-2016
Date: 28-8-2018
Date: 18-5-2017
|
Protons and other electrophiles are not the only reactive species that initiate addition reactions to carbon-carbon double bonds. Curiously, this first became evident as a result of conflicting reports concerning the regioselectivity of HBr additions. As noted earlier, the acid-induced addition of HBr to 1-butene gave predominantly 2-bromobutane, the Markovnikov Rule product. However, in some early experiments in which peroxide contaminated reactants were used, 1-bromobutane was the chief product. Further study showed that an alternative radical chain-reaction, initiated by peroxides, was responsible for the anti-Markovnikov product. This is shown by the following equations.
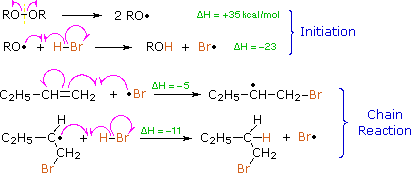
The weak O–O bond of a peroxide initiator is broken homolytically by thermal or hight energy. The resulting alkoxy radical then abstracts a hydrogen atom from HBr in a strongly exothermic reaction. Once a bromine atom is formed it adds to the π-bond of the alkene in the first step of a chain reaction. This addition is regioselective, giving the more stable carbon radical as an intermediate. The second step is carbon radical abstraction of another hydrogen from HBr, generating the anti-Markovnikov alkyl bromide and a new bromine atom. Each of the steps in this chain reaction is exothermic, so once started the process continues until radicals are lost to termination events.
This free radical chain addition competes very favorably with the slower ionic addition of HBr described earlier, especially in non-polar solvents. It is important to note, however, that HBr is unique in this respect. The radical addition process is unfavorable for HCl and HI because one of the chain steps becomes endothermic (the second for HCl & the first for HI).
Other radical addition reactions to alkenes have been observed, one example being the peroxide induced addition of carbon tetrachloride shown in the following equation
| RCH=CH2 + CCl4 (peroxide initiator) —> RCHClCH2CCl3 |
The best known and most important use of free radical addition to alkenes is probably polymerization. Since the addition of carbon radicals to double bonds is energetically favorable, concentrated solutions of alkenes are prone to radical-initiated polymerization, as illustrated for propene by the following equation. The blue colored R-group represents an initiating radical species or a growing polymer chain; the propene monomers are colored maroon. The addition always occurs so that the more stable radical intermediate is formed.
| RCH2(CH3)CH· + CH3CH=CH2 —> RCH2(CH3)CH-CH2(CH3)CH· + CH3CH=CH2 —> RCH2(CH3)CHCH2(CH3)CH-CH2(CH3)CH· —> etc. |



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|