
آخر المواضيع المضافة


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 11-6-2018
Date: 3-7-2018
Date: 24-5-2018
|
If one solution ( ) to a second-order ordinary differential equation
) to a second-order ordinary differential equation
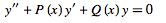 |
(1) |
is known, the other ( ) may be found using the so-called reduction of order method. From Abel's differential equation identity
) may be found using the so-called reduction of order method. From Abel's differential equation identity
 |
(2) |
where
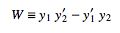 |
(3) |
is the Wronskian.
Integrating gives
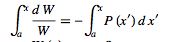 |
(4) |
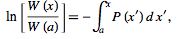 |
(5) |
and solving for  gives
gives
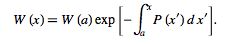 |
(6) |
But
 |
(7) |
so combining (◇) and (◇) yields
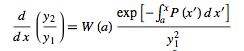 |
(8) |
 |
(9) |
Disregarding  , since it is simply a multiplicative constant, and the constants
, since it is simply a multiplicative constant, and the constants  and
and  , which will contribute a solution which is not linearly independent of
, which will contribute a solution which is not linearly independent of  , leaves
, leaves
 |
(10) |
In the special case  , this simplifies to
, this simplifies to
 |
(11) |
If both general solutions to a second-order nonhomogeneous differential equation are known, variation of parameters can be used to find the particular solution.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|