


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 26-11-2019
Date: 23-10-2019
Date: 25-11-2019
|
Lewis Acids and the Curved Arrow Formalism
The fact that a Lewis acid is able to accept an electron pair means that it must have either a vacant, low-energy orbital or a polar bond to hydrogen so that it can donate H+ (which has an empty 1s orbital). Thus, the Lewis definition of acidity includes many species in addition to H+. For example, various metal cations, such as Mg+2, are Lewis acids because they accept a pair of electrons when they form a bond to a base. theire are certain metabolic reactions begin with an acid–base reaction between Mg+2 as a Lewis acid and an organic diphosphate or triphosphate ion as the Lewis base.
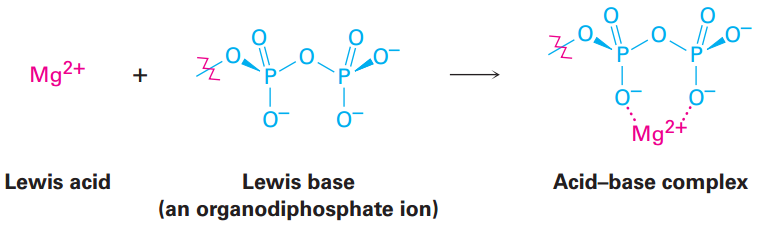
In the same way, compounds of group 3A elements, such as BF3and AlCl3, are Lewis acids because they have unfilled valence orbitals and can accept electron pairs from Lewis bases, as shown in FIGURE 1.1. Similarly, many transition metal compounds, such as TiCl4, FeCl3, ZnCl2, and SnCl4, are Lewis acids
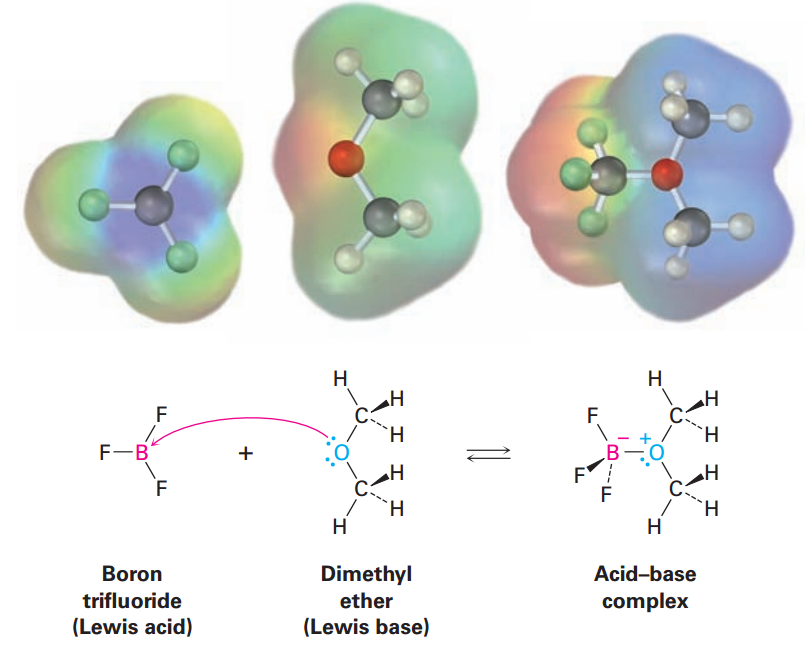
FIGURE 1.1 The reaction of boron trifluoride, a Lewis acid, with dimethyl ether, a Lewis base. The Lewis acid accepts a pair of electrons, and the Lewis base donates a pair of nonbonding electrons. Note how the movement of electrons fromthe Lewis base tothe Lewis acid is indicated by a curved arrow. Note also how, in electrostatic potential maps, the boron becomes more negative (red)after reaction because it has gained electrons and the oxygen atom becomes more positive (blue) because it has donated electrons.
Look closely at the acid–base reaction in Figure 1.1, and note how it is shown. Dimethyl ether, the Lewis base, donates an electron pair to a vacant valence orbital of the boron atom in BF3, a Lewis acid. The direction of electron-pair flow from base to acid is shown using curved arrows, just as the direction of electron flow from one resonance structure to another was shown using curved arrows in Section 1.1. A curved arrow always means that a pair of electrons moves from the atom at the tail of the arrow to the atom at the head of the arrow .We’ll use this curved-arrow notation throughout the remainder of this text to indicate electron flow during reactions. Some further examples of Lewis acids follow:
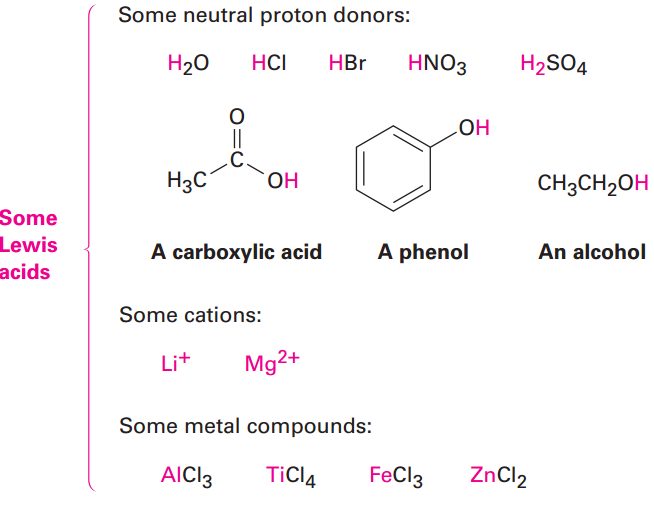



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|