


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 31-8-2017
Date: 21-8-2017
Date: 22-8-2017
|
Acetic Acid 231
Currently, the major route for obtaining acetic acid (ethanoic acid) is the carbonylation of methanol. It may also be produced by the catalyzed oxidation of n-butane.
The production of acetic acid from n-butene mixture is a vapor-phase catalytic process. The oxidation reaction occurs at approximately 270°C over a titanium vanadate catalyst. A 70% acetic acid yield has been reported. The major by-products are carbon oxides (25%) and maleic anhydride (3%):
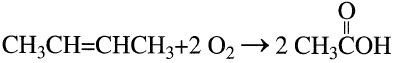
Acetic acid may also be produced by reacting a mixture of n-butenes with acetic acid over an ion exchange resin. The formed sec-butyl acetate is then oxidized to yield three moles of acetic acid:
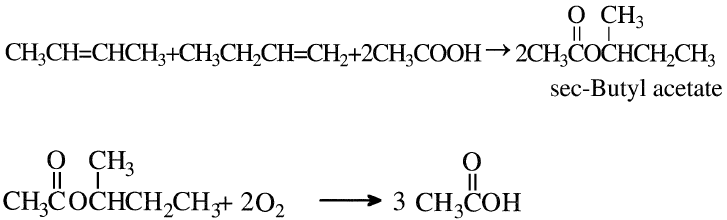
The reaction conditions are approximately 100–120°C and 15–25 atmospheres. The oxidation step is noncatalytic and occurs at approximately 200°C and 60 atmospheres. An acetic acid yield of 58% could be obtained. By-products are formic acid (6%), higher boiling compounds (3%), and carbon oxides (28%). Figure 1-1 shows the Bayer AG two-step process for producing acetic acid from n-butenes.
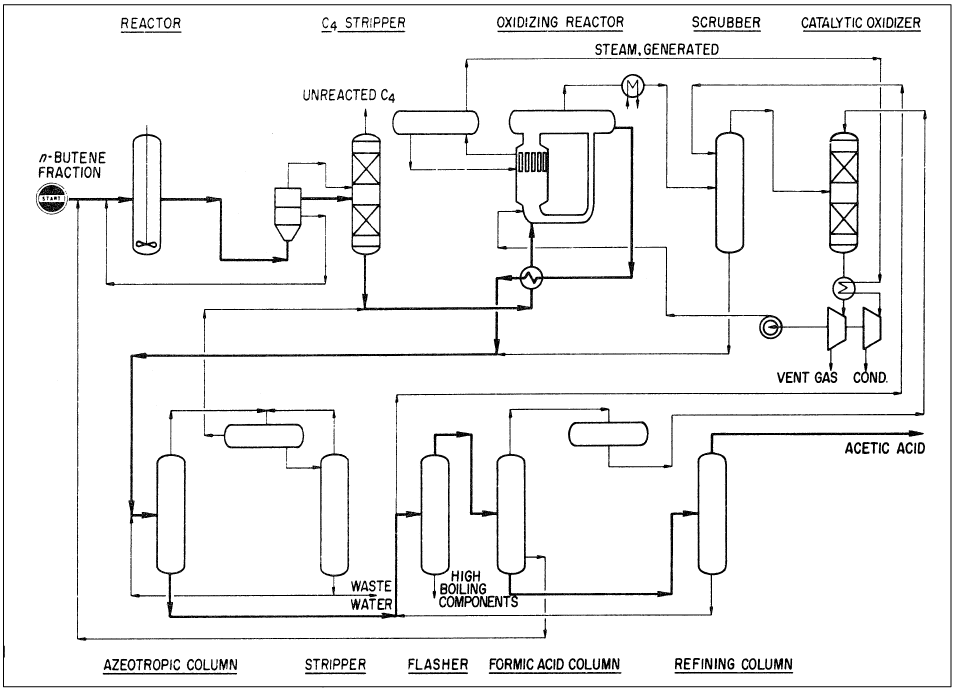
Figure 1-1. The Bayer AG two-step process for producing acetic acid from n-butenes.
Acetic acid is a versatile reagent. It is an important esterifying agent for the manufacture of cellulose acetate (for acetate fibers and lacquers), vinyl acetate monomer, and ethyl and butyl acetates. Acetic acid is used to produce pharmaceuticals, insecticides, and dyes. It is also a precursor for chloroacetic acid and acetic anhydride. The 1114 U.S. production of acetic acid was approximately 4 billion pounds.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تُطلق فعّاليات مؤتمر ذاكرة الألم في العراق
|
|
|