


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 22-8-2017
Date: 16-8-2017
Date: 31-8-2017
|
Oligomerization of Olefins (Dimerization)
This process produces polymer gasoline with a high octane. Dimerization was first used (1935) to dimerize isobutylene to diisobutylene, constituted of 2,4,4-trimethyl-1-pentene (80%) and 2,4,4-trimethyl-2- pentene (20%). Both phosphoric and sulfuric acid were used as catalysts. At present, the feedstock is either a propylene-propane mixture or propylene-butane mixture where propane and butane are diluents. The product is an olefin having a high octane number. When propylene is used, a trimer or a tetramer is formed. The polymerization reaction is highly exothermic, so the temperature has to be controlled. The presence of propane and butane in the mixture acts as a heat sink to absorb part of the reaction heat. Typical reaction conditions are 170–250°C and 25–100 atm.
The polymerization reaction starts by protonating the olefin and forming a carbocation. For example, protonating propene gives isopropyl carbocation. The proton is provided by the ionization of phosphoric acid:

The next step is the reaction of the carbocation with the olefin (propene or butene).
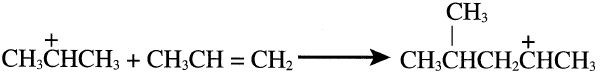
The newly-formed carbocation either eliminates a proton and forms a dimer or attacks another propene molecule and eliminates a proton, giving the trimer.
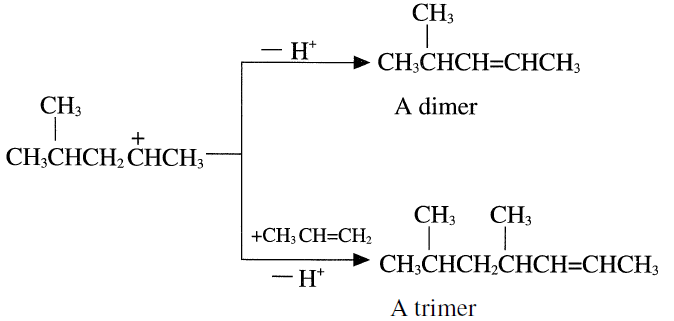
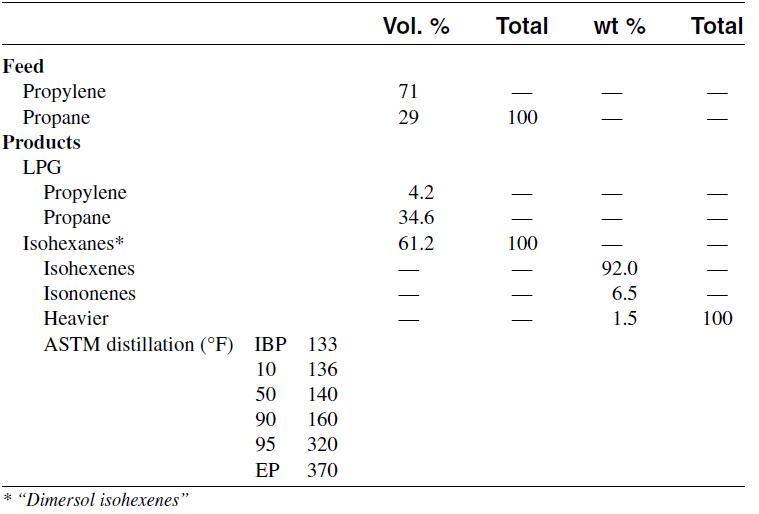
Further protonation of the trimer produces a C9 carbocation which may further react with another propene molecule and eventually produce propylene tetramer. The product is a mixture of dimers, trimers, tetramers, and pentamers having an average RON (Research Octane Number) = 95. Table 1.1 shows the analysis of feed and products from dimerization of propylene.
Table 1.1 Typical feed and products from the dimerization of propylene
The most important olefins and diolefins used to manufacture petrochemicals are ethylene, propylene, butylenes, and butadiene. Butadiene, a conjugated diolefin, is normally coproduced with C2–C4 olefins from different cracking processes. Separation of these olefins from catalytic and thermal cracking gas streams could be achieved using physical and chemical separation methods. However, the petrochemical demand for olefins is much greater than the amounts these operations produce. Most olefins and butadienes are produced by steam cracking hydrocarbons.
Butadiene can be alternatively produced by other synthetic routes discussed with the synthesis of isoprene, the second major diolefin for rubber production.



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
لتعزيز التواصل مع الزائرات الأجنبيات : العتبة العلويّة المقدّسة تُطلق دورة لتعليم اللغة الإنجليزية لخادمات القسم النسويّ
|
|
|