


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 17-4-2017
Date: 29-3-2017
Date: 25-4-2017
|
Binding Energy
The loss in mass, or mass defect, is due to the conversion of mass to binding energy when the nucleus is formed. Binding energy is defined as the amount of energy that must be supplied to a nucleus to completely separate its nuclear particles (nucleons). It can also be understood as the amount of energy that would be released if the nucleus was formed from the separate particles. Binding energy is the energy equivalent of the mass defect. Since the mass defect was converted to binding energy (BE) when the nucleus was formed, it is possible to calculate the binding energy using a conversion factor derived by the mass-energy relationship from Einstein's Theory of Relativity.
Einstein's famous equation relating mass and energy is E = mc2 where c is the velocity of light (c = 2.998 x 108 m/sec). The energy equivalent of 1 amu can be determined by inserting this quantity of mass into Einstein's equation and applying conversion factors.
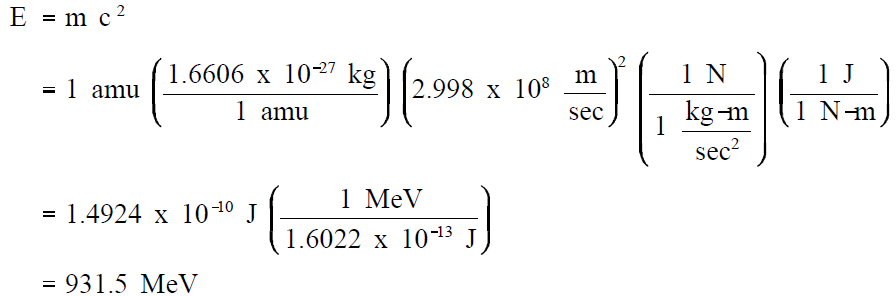
Conversion Factors:
1 amu = 1.6606 x 10 -27 kg
1 newton = 1 kg-m/sec2
1 joule = 1 newton-meter
1 MeV = 1.6022 x 10-13 joules
Since 1 amu is equivalent to 931.5 MeV of energy, the binding energy can be calculated using Equation (1-1).
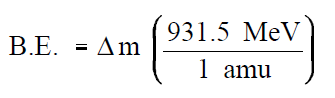 (1-1)
(1-1)



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|