
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Ohms law
المؤلف:
Richard Fitzpatrick
المصدر:
Classical Electromagnetism
الجزء والصفحة:
p 152
4-1-2017
3064
Ohm's law
We all know the simplest version of Ohm's law:
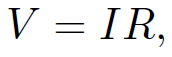 (1.1)
(1.1)
where V is the voltage drop across a resistor of resistance R when a current I flows through it. Let us generalize this law so that it is expressed in terms of E and j rather than V and I. Consider a length l of a conductor of uniform cross-sectional area A with a current I flowing down it. In general, we expect the electrical resistance of the conductor to be proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its area (i.e., it is harder to push an electrical current down a long rather than a short wire, and it is easier to push a current down a wide rather than a narrow conducting channel.) Thus, we can write
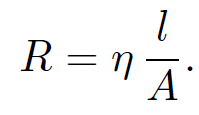 (1.2)
(1.2)
The constant ƞ is called the resistivity and is measured in units of ohm-meters. Ohm's law becomes
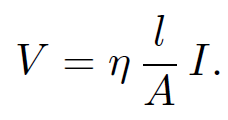 (1.3)
(1.3)
However, I/A = jz (suppose that the conductor is aligned along the z-axis) and V/l = Ez, so the above equation reduces to
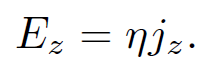 (1.4)
(1.4)
There is nothing special about the z-axis (in an isotropic conducting medium) so the previous formula immediately generalizes to
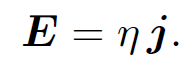 (1.5)
(1.5)
This is the vector form of Ohm's law. A charge q which moves through a voltage drop V acquires an energy qV from the electric field. In a resistor this energy is dissipated as heat. This type of heating is called ''ohmic heating". Suppose that N charges per unit time pass through a resistor. The current flowing is obviously I = Nq. The total energy gained by the charges, which appears as heat inside the resistor, is
 (1.6)
(1.6)
per unit time. Thus, the heating power is
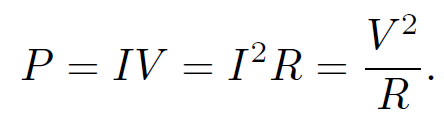 (1.7)
(1.7)
Equations (1.6) and (1.7) generalize to
 (1.8)
(1.8)
where P is now the power dissipated per unit volume in a resistive medium.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















