

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
RELAY CIRCUITS AND CONTROL PROBLEMS-Special problems involving the design of relay circuits
المؤلف:
J. ELDON WHITESITT
المصدر:
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS
الجزء والصفحة:
150-153
4-1-2017
1721
This final section on relay circuits contains two examples in which the sequence diagram is not given but the situation calls for the construction of a sequence diagram as part of the solution to the problem. This situation is more realistic than those of Section (Design of sequential relay circuits from given conditions) and corresponds closely to the problem which faces the designer in practical applications of the techniques we have presented.
Suppose that it is desired to obtain four or more signals from two keys in such a way that no signal is given when both keys are in released position. Combinational circuits alone will not solve the problem since there are only four states possible for two switches and one of these (both released) is specifically excluded. Sequential signals, using secondary relays, must therefore be used. The problem is made more specific in the following example.
EXAMPLE 1. Design a sequential circuit to cause four lights, red, white, blue, and green, respectively, to flash individually.

FIG. 1-1. Sequence diagram for four signals from two keys.
Solution. Many sequential inputs could be chosen, but those of Fig. 5-38 are a reasonable choice. The input combinations based on keys A and B are simple enough to be easily learned, but complex enough to make control of secondary relays easy. The four sequences are the signals in time intervals 2-4, 6-8, 10-12, and 14-16, respectively. An interval in which both keys are released is shown between each sequence since we will permit the sequences to occur in an arbitrary order. Because of this, it is necessary to cause all secondary relays, as well, to release in intervals 5, 9, 13, and 17. A suitable sequence of operation is shown for secondary relays X and Y which will distinguish between the four signals. The red light will be controlled by an output in 4, the blue light by anoutput in 8, the white light by an output in 12, and the green light by an output in 16. The output functions are Fr = a'bzy, Fw = ab'xy, Fb = ab'x'y, and Fg = a'bx'y. The control functions for relays X and F are Fz = ab'y' - (a + b)x and Fy = ab + (a + b)y. The corresponding circuit is left to the reader.
EXAMPLE 2. An electric combination lock is to be designed based on five visible keys A, B, C, D, and E and too hidden keys F and G. A solenoid is to withdraw the bolt when keys B E A D are pressed consecutively, in that order only. (The solenoid is operated by current through its winding.) A burglar alarm is to sound if any error is made in manipulation of the keys. Key F is to shut off the alarm and release all secondary relays. Key G is to reset the lock.
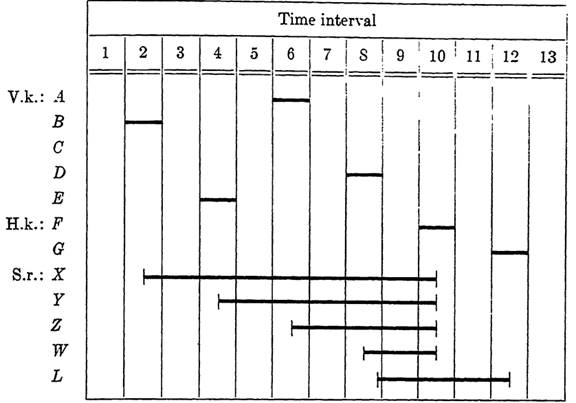
FIG. 1-2. Sequence diagram for the combination lock of Example 2. V.k. and H. k. denote visible and hidden keys.
Solution. First we will arrange two relays, T to operate the alarm, and L to operate the solenoid which releases the lock. This is done through make contacts on the relays. The reason for using relays here is that they permit locking paths to be introduced to maintain operation until the appropriate key is depressed to cause release of these devices. Figure 5-39 shows the correct operating sequence for operation of L and all secondary relays needed, except the one used to control the alarm. The latter cannot be shown without drawing all incorrect sequences as well.
The control functions are then given by
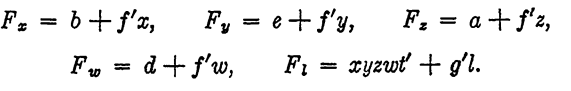
Here the t' in the control function for L guarantees that the lock bolt will never be withdrawn if the alarm is sounding. Finally, the alarm relay T is controlled by
Ft= c+x'y+ y'z+z'w+f't.
Note that the alarm will ring in case an error of any type is made. From these functions, the circuit can be readily drawn. This is left to the reader.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجبر البولياني
الاكثر قراءة في الجبر البولياني
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















