
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Retarded fields
المؤلف:
Richard Fitzpatrick
المصدر:
Classical Electromagnetism
الجزء والصفحة:
p 139
3-1-2017
2714
Retarded fields
We know the solution to Maxwell's equations in terms of retarded potentials. Let us now construct the associated electric and magnetic fields using
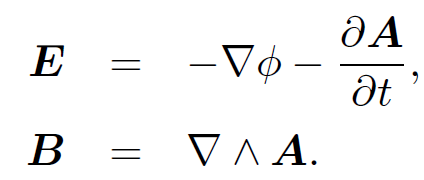 (1.1)
(1.1)
It is helpful to write
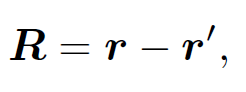 (1.2)
(1.2)
where R = |r - rʹ|. The retarded time becomes tr = t – R/c, and a general retarded quantity is written [F(r, t)] ≡ F(r, tr). Thus, we can write the retarded potential solutions of Maxwell's equations in the especially compact form:
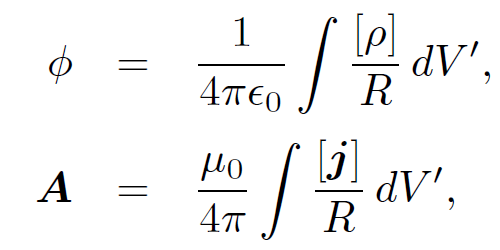 (1.3)
(1.3)
where dVʹ ≡ d3rʹ. It is easily seen that
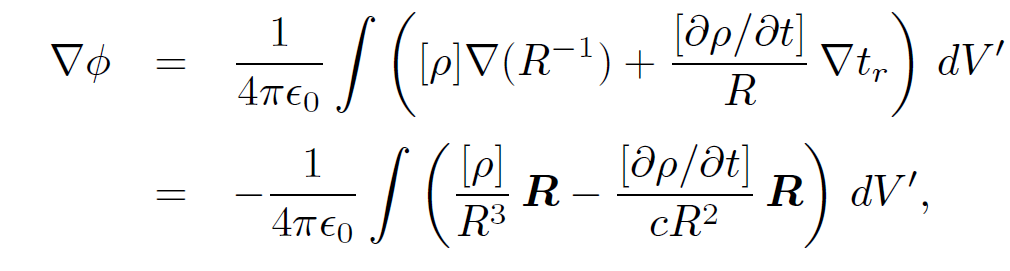 (1.4)
(1.4)
where use has been made of
 (1.5)
(1.5)
Likewise,
 (1.6)
(1.6)
Equations (1.1), (1.4), and (1.6) can be combined to give
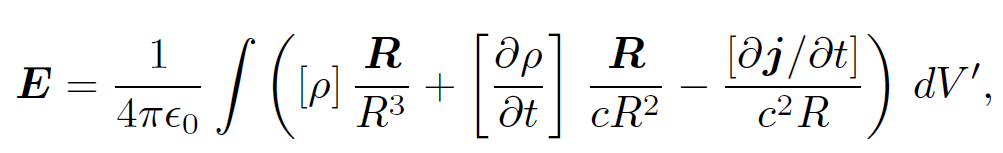 (1.7)
(1.7)
which is the time dependent generalization of Coulomb's law, and
 (1.8)
(1.8)
which is the time dependent generalization of the Biot-Savart law. Suppose that the typical variation time-scale of our charges and currents is tʹ. Let us define Rʹ = c tʹ which is the distance a light ray travels in time tʹ. We can evaluate Eqs. (1.7) and (1.8) in two asymptotic limits: the ''near field" region R << Rʹ, and the ''far field" region R >> Rʹ. In the near field region
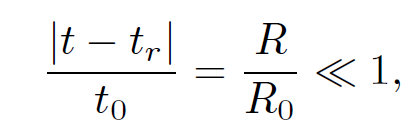 (1.9)
(1.9)
so the difference between retarded time and standard time is relatively small. This allows us to expand retarded quantities in a Taylor series. Thus,
 (1.10)
(1.10)
giving
 (1.11)
(1.11)
Expansion of the retarded quantities in the near field region yields
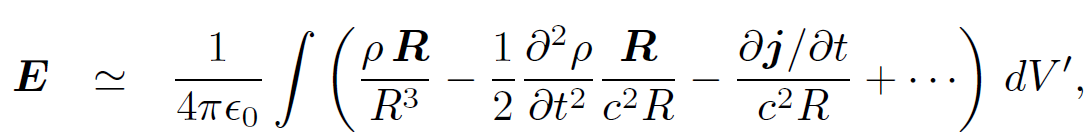 (1.12a)
(1.12a)
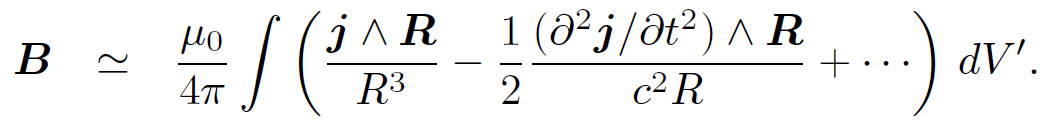 (1.12b)
(1.12b)
In Eq. (1.12a) the first term on the right-hand side corresponds to Coulomb's law, the second term is the correction due to retardation effects, and the third term corresponds to Faraday induction. In Eq. (1.12b) the first term on the right-hand side is the Biot-Savart law and the second term is the correction due to retardation effects. Note that the retardation corrections are only of order (R/R0)2. We might suppose, from looking at Eqs. (1.7) and (1.8), that the corrections should be of order R/R0, however all of the order R/R0 terms canceled out in the previous expansion. Suppose, then, that we have a d.c. circuit sitting on a laboratory benchtop. Let the currents in the circuit change on a typical time-scale of one tenth of a second. In this time light can travel about 3×107 meters, so R0 ~ 30. 000 kilometers. The length-scale of the experiment is about one meter, so R = 1 meter. Thus, the retardation corrections are of order (3 × 107)-2 ~ 10-15. It is clear that we are fairly safe just using Coulomb's law, Faraday's law, and the Biot-Savart law to analyze the fields generated by this type of circuit. In the far field region, R >> R0, Eqs. (1.7) and (1.8) are dominated by the terms which vary like R-1, so
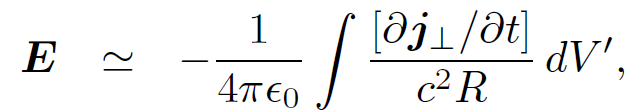 (1.13a)
(1.13a)
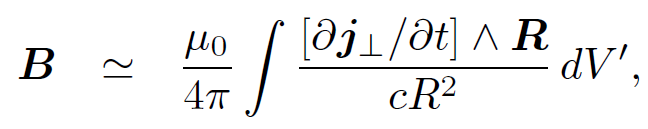 (1.13b)
(1.13b)
where
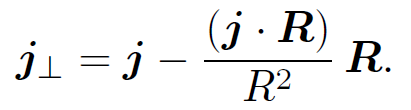 (1.13c)
(1.13c)
Here, use has been made of [∂ρ/∂t] = -[∇ . j] and [∇ . j] = -[∂j/∂t] . R/cR + O(1/R2). Suppose that our charges and currents are localized to some region in the vicinity of rʹ = r*. Let R* = r - r*, with R* = |r - r*|. Suppose that the extent of the current and charge containing region is much less than R*. It follows that retarded quantities can be written
 (1.14)
(1.14)
etc. Thus, the electric field reduces to
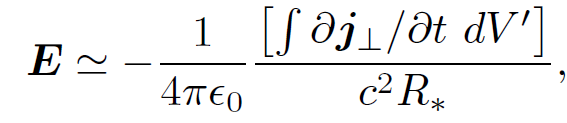 (1.15)
(1.15)
whereas the magnetic field is given by
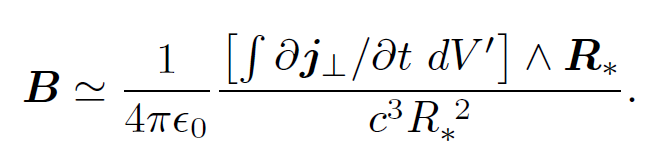 (1.16)
(1.16)
Note that
 (1.17)
(1.17)
and
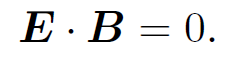 (1.18)
(1.18)
This configuration of electric and magnetic fields is characteristic of an electromagnetic wave. Thus, Eqs. (1.17) and (1.18) describe an electromagnetic wave propagating radially away from the charge and current containing region. Note that the wave is driven by time varying electric currents. Now, charges moving with a constant velocity constitute a steady current, so a non-steady current is associated with accelerating charges. We conclude that accelerating electric charges emit electromagnetic waves. The wave fields, (1.15) and (1.16), fall off like the inverse of the distance from the wave source. This behaviour should be contrasted with that of Coulomb or Biot-Savart fields which fall off like the inverse square of the distance from the source. The fact that wave fields attenuate fairly gently with increasing distance from the source is what makes astronomy possible. If wave fields obeyed an inverse square law then no appreciable radiation would reach us from the rest of the universe. In conclusion, electric and magnetic fields look simple in the near field region (they are just Coulomb fields, etc.) and also in the far field region (they are just electromagnetic waves). Only in the intermediate region, R ~ R0, do things start getting really complicated (so we do not look in this region!).
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















