


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 25-7-2016
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 14-8-2016
|
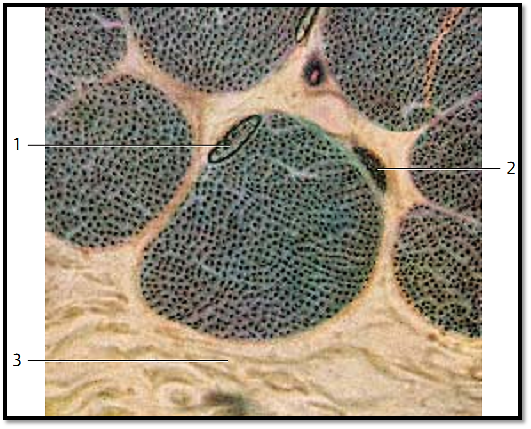
Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
Cross-section of skeletal muscle fibers with evenly distribute d myofibrils that are not bundle d (simple fibril pattern). Note the long, oval nuclei close to the cell surface 1 in the muscle fiber. The two darker-stained nuclei in the connective tissue belong to f ibrocytes 2 .
1 Nucleus in a muscle fiber
2 Fibrocyte
3 Collagenous (dense) connective tissue
Stain: Heidenhain iron hematoxylin; magnification: × 1125
Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
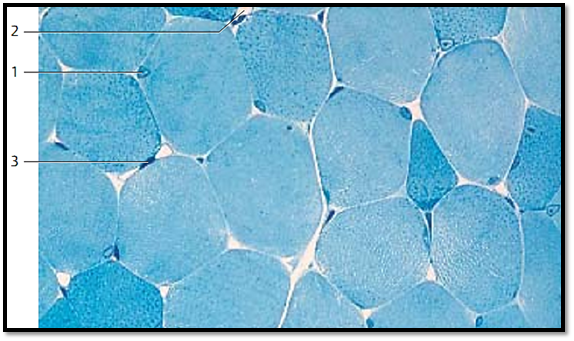
This cross-section shows striate d muscle fibers about 10–10 0 μm thick . Size and morphology depend on muscle function and workload. The nuclei 1 are clearly locate d in the periphery of the cells. The plasmalemma envelops the cytoplasm ( sarcoplasm). The crevices between the muscle fibers contain the loose connective tissue of the endomysium , which consists mostly of reticular fibers. The even, dense and only softly stained dots in this cross-section reflect the even distribution of myofibrils . Occasionally, dependent on the fixation, the fibrils show a grouping pattern (Cohnheim’s fields, groups ). The plasmalemma is of ten called sarcolemma. This terminology was coined in light microscopy. In fact, the sarcolemma consists of the plasmalemma, the basal lamina and a network of delicate reticular f ibers. These are not distinct components in light microscopic evaluations.
1 Nucleus of a skeletal muscle fiber
2 Capillary
3 Nucleus of a connective tissue cell
Semi-thin section; stain: methylene blue-azure II; magnification: × 800
Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
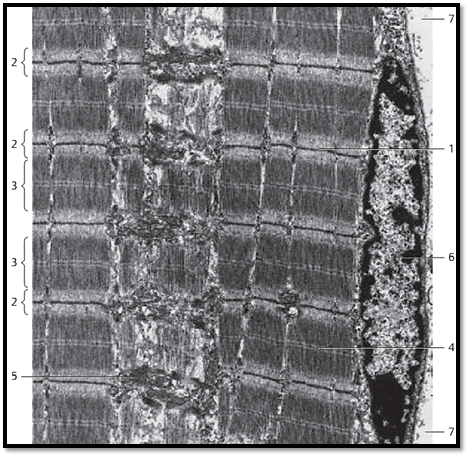
Longitudinal section through striate d myofibrils with conspicuous sarcomere organization. A sarcomere extends from one Z-band 1 to the next 1 . In Z-bands, the actin filaments of two successive sarcomeres twist together and are cross-linked. Actin filaments in the form of I-bands (isotropic bands) flank both sides of the Z-band 2 . The thicker myosin filaments form the A-band (anisotropic band) 3 of the myofibril. Actin and myosin filaments form a twisted helix and leave only the H-band 4 (light zone) in the middle of the A-band. The H-band consists only of myosin filaments, the I-bands only of actin filaments. The dark centerline in the H-zone is the center membrane . Cross-linking of the myosin filaments creates this line. Note the peripheral nucleus 6 close to the fiber surface under the sarcolemma (plasmalemma).
1 Z-band
2 I-bands (isotropic)
3 A -bands (anisotropic)
4 H-band (H-zone; Hensen’s bands) with M-band (M-line)
5 Mitochondria
6 Nucleus of the muscle fiber
7 Extracellular matrix with collagen fibrils
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 6000
Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
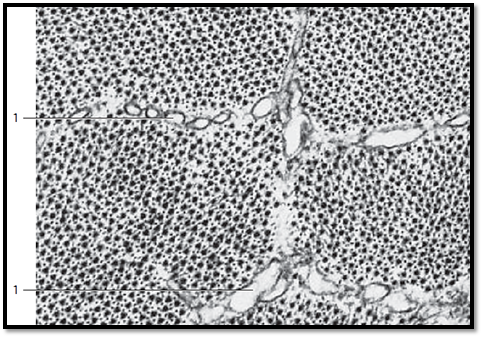
Longitudinal section through several sarcomeres in a skeletal muscle fibril . The space between two adjacent Z-bands 1 is called sarcomere.
By this definition, a sarcomere consists of an A-band and the two halves of the adjacent I-band 2 on each side. The Z-band 1 is electron-dense. It runs through the center of the I-band 2 . The somewhat lighter stained H-band goes through the middle of the A-band 3 . In the center of the H-band is the M-band or M-line (center membrane) . Between neighboring A-bands are cuts through smooth ER membranes (sarcoplasmic reticulum = L -system). Crista-type mitochondria occur at the level of the I-bands.
1 Z-bands or Z-disk
2 I-bands (isotropic)
3 A -bands (anisotropic)
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 25000

Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
Cross-section through bundles of myofibrils at the level of an A-band and the T-tubules 1 that cover the myofibril borders. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum, here called sarcoplasmic reticulum (sarcotubular system ), forms a network around ever y myofibril as longitudinal system ( L -system ) and trans-verse system (T-tubules, T-system ). Note the hexagonal organization of the thick myosin filaments and the fine spot-like structures, which correspond to cross-sectioned thin actin filaments. There are actin and myosin filaments. Actin filaments are thin (7 nm), about 1 μm in length, and consist of actin, tropomyosin and troponin. Myosin filaments are built from light and heavy meromyosin (about 1.5 μm long).
1 T-tubules (transverse system)
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 46000
Striated Muscle—Psoas Muscle
The sarcoplasm of striate d muscle fibers contains mitochondria ( sarcosomes) . They can be made visible by marker enzyme histochemistry. The enzyme succinate dehydrogenase is a marker enzyme for mitochondria. Its localization is shown in this freeze-fracture preparation. The products of the histochemical reaction accumulate in the locations of mitochondria. In cross-sections, sarcosome-rich fibers ( aerobic f ibers ) appear dark and densely granulated, the sarcosome-poor fibers ( anaerobic f ibers) appear light. The nuclei are not visible with this marker enzyme me diated visualization. A staining method for the nuclei was not added after the histochemical procedure.
Histochemical reaction of the marker enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (SDH); magnification: × 130

References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgar t · New York .



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
عوائل الشهداء: العتبة العباسية المقدسة سبّاقة في استذكار شهداء العراق عبر فعالياتها وأنشطتها المختلفة
|
|
|