


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية| Plate count method ISO 13720:2010 for presumptive Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 2025-02-23
Date: 17-3-2016
Date: 18-3-2016
|
Plate count method ISO 13720:2010 for presumptive Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products
This method of the International Organization for Standardization is applicable to meat and meat products, including poultry.
1. Material required for analysis
Preparation of the sample and serial dilutions
• Diluent: Saline Peptone Water (SPW) or Buffered Peptone Water (BPW)
• Dilution tubes containing 9 ml of Saline Peptone Water (SPW) or Buffered Peptone Water (BPW)
Enumeration of presumptive Pseudomonas spp.
• Cephalothin Sodium Fusidate Cetrimide (CFC) Agar
• Oxidase Kovacs Reagent
• Laboratory incubator set to 25 ± 1°C
2. Procedure
A general flowchart for the enumeration of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products using the plate count method ISO 13720:2010 is shown in Figure 1.
a) Preparation of the samples, inoculation and incubation: For the preparation of the sample and serial dilutions . Select three appropriate dilutions of the sample and inoculate 0.1 ml of each dilution on Cephalothin Sodium Fusidate Cetrimide (CFC) Agar plates, using the spread plating technique.
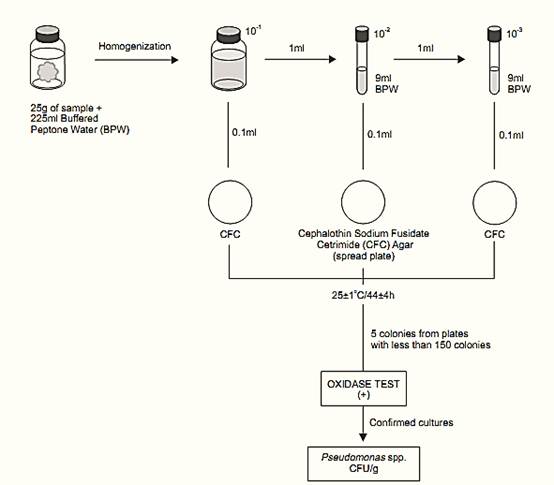
Figure 1 Scheme of analysis for the enumeration of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products using the plate count method ISO 13720:2010.
Note a.1) Three dilutions are the number usually inoculated, but the ISO 7218:2007 allows the inoculation of less than three dilutions. When at least two successive dilutions are inoculated, only one plate per dilution is required. If only one dilution is inoculated, then two plates are required.
Incubate the plates inverted at 25 ± 1°C/44 ± 4 h. Count all the colonies on each plate and select plates with less than 150 colonies for confirmation.
b) Confirmation: From each plate with less than 150 colonies, select five for confirmation. If there are fewer than five, select all. Include all colony types from each retained plate for confirmation.
b.1) Oxidase test: Using a platinum/iridium loop or glass rod, take a portion the colony and streak it onto a filter paper moistened with the Oxidase Kovacs Reagent. The appearance of a violet to purple color within 10s indicates a positive reaction. If the color has not changed after 30s, the test is considered negative.
c) Calculation of the results: Consider as presumptive Pseudomonas spp. the cultures showing positive oxidase test.
c.1) First it is necessary to calculate the number of colonies of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. present in each plate retained for count (all the plates containing less than 150 colonies). Use the formula below for this calculation and round the result to a whole number.
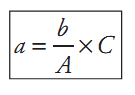
a = number of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. in the plate
b = number of colonies confirmed
A = number of colonies tested
C = total number of colonies counted
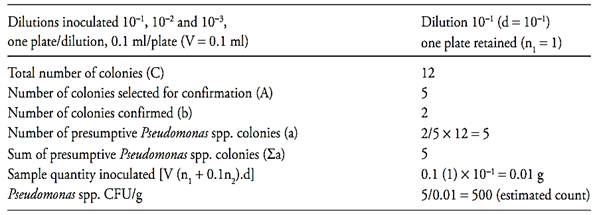
Example: Total number of colonies in a plate (C) = 139; number of colonies selected for confirmation (A) = 5; number of colonies confirmed (b) = 4. Number of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. colonies in the plate (a) = 139 × 4/5 = 111.
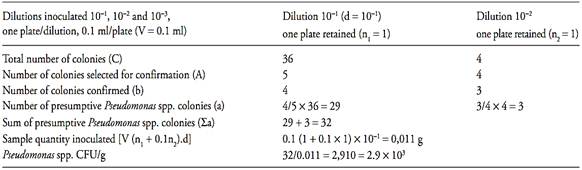
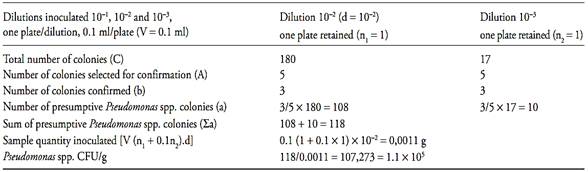
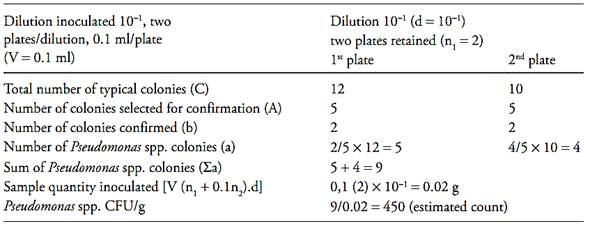
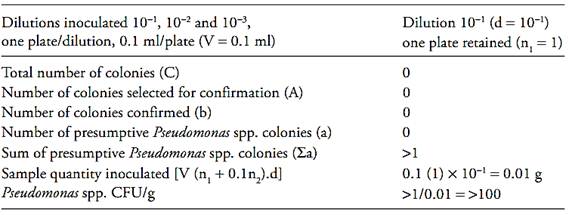
c.2) after that it is necessary to calculate the number of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. colony forming units (CFU) per gram or milliliter of the sample, witch is the sum of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. colonies (a) obtained in each plate divided for the sum of sample quantity inoculated in each plate. Use the formula below for this calculation and round the result to a whole number (examples 1 and 2)
Example 1
Example 2
Example 3
Example 4
Example 5
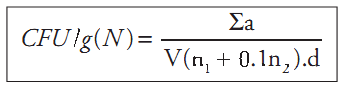
Σa = Sum of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. colonies in each plate
V = Volume of inoculum in each plate
n1 = number of plate retained at the first dilution counted
n2 = number of plate retained at the second dilution counted
d = dilution factor corresponding to the first dilution retained
If the dishe (s) at the level of the initial suspension contain less than 15 colonies of presumptive Pseudomonas spp., calculate the result as described above and report the count as estimated (examples 3 and 4). If the dishe(s) at the level of the initial suspension do not contain any colonies, calculate the result as described above for one colony and report the count as “less than the value obtained” (example 5).
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
International Organization for Standardization (2010) ISO 13720:2010. Meat and meat products – Enumeration of presumptive Pseudomonas spp. Geneva, ISO.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|