


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-03-23
Date: 2024-07-02
Date: 2024-04-17
|
/θ, ð/
In Scottish Standard English /θ, ð/ are realized as voiceless dental fricatives. In Urban Scots /θ/ has the traditional variant [h], in e.g. think, something, which may also be completely deleted in e.g. think, both, and a possible retroflex or alveolo-palatal fricative or 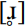 in the initial cluster /θr/ , in e.g. three (Wells 1982: 410; Macafee 1983: 33). Macafee (1983: 34) noted sporadic instances of /f/ for /θ/ in Glasgow. By the time of the collection of the 1997 Glasgow corpus [f] had emerged as a variable but frequent variant in the speech of working-class adolescents (Stuart-Smith 1999: 209). Interestingly [f] is added to the existing Scots variants to form a constellation of ‘non-standard’ variants for /θ/ such that in spontaneous speech [θ] accounts for less than a third of the overall variation in these speakers.
in the initial cluster /θr/ , in e.g. three (Wells 1982: 410; Macafee 1983: 33). Macafee (1983: 34) noted sporadic instances of /f/ for /θ/ in Glasgow. By the time of the collection of the 1997 Glasgow corpus [f] had emerged as a variable but frequent variant in the speech of working-class adolescents (Stuart-Smith 1999: 209). Interestingly [f] is added to the existing Scots variants to form a constellation of ‘non-standard’ variants for /θ/ such that in spontaneous speech [θ] accounts for less than a third of the overall variation in these speakers.
The traditional Urban Scots variant for /ð/ , particularly in intervocalic position, is the tap [R], in e.g. brother, though complete elision is also common, in e.g. the tag, an(d th)at (Wells 1982: 410; Johnston 1997: 508). Again the working-class adolescents in the 1997 Glasgow sample showed [v] for /ð/ in words such as smooth; [v] joins the traditional Scots variants to extend the array of possible ‘non-standard’ variation, though unlike /θ/ this makes up a much smaller proportion of the variation (under 20%).
Stopping of /θ, ð/ occurs occasionally in Scots in Glasgow (Johnston 1997: 506) where it may be due to Irish/Ulster influence.
|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|