


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2025-02-24
Date: 2024-04-06
Date: 2024-06-25
|
For a bilabial sound, the active articulator is the bottom lip, and the passive articulator is the top lip.

There is at least one further English phoneme which to an extent fits under this heading: this is the approximant /w/ in wet. In producing [w], the lips are certainly approximated, though not enough to cause friction or obstruct the airflow; but you should be able to feel that the back of your tongue is also bunched up. This additional articulation takes place at the velum, so that [w] is not simply a labial sound, but a labial-velar one. In some accents of English, notably those spoken in Scotland and New Zealand, this /w/ contrasts with /M/, the voiceless labial-velar fricative, which tends to occur in words spelled . If you have the same pronunciation for witch and which, or Wales and whales, then you have only /w/; if these are consistently different for you, then these minimal pairs establish a contrast of /w/ and /M/.
. If you have the same pronunciation for witch and which, or Wales and whales, then you have only /w/; if these are consistently different for you, then these minimal pairs establish a contrast of /w/ and /M/.
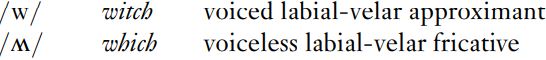
|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن مؤتمر ذاكرة الألم في العراق ورقة بحثية تتناول الأهداف والاستراتيجيات التي يعتمدها كرسي اليونسكو لتطوير دراسات حوار الأديان
|
|
|