

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Schemas and scripts
المؤلف:
George Yule
المصدر:
The study of language
الجزء والصفحة:
150-11
21-2-2022
5033
Schemas and scripts
A schema is a general term for a conventional knowledge structure that exists in memory. We were using our conventional knowledge of what a school classroom is like, or a “classroom schema,” as we tried to make sense of the previous example. We have many schemas (or schemata) that are used in the interpretation of what we experience and what we hear or read about. If you hear someone describe what happened during a visit to a supermarket, you don’t have to be told what is normally found in a supermarket. You already have a “supermarket schema” (food displayed on shelves, arranged in aisles, shopping carts and baskets, check-out counter, and other conventional features) as part of your background knowledge.
Similar in many ways to a schema is a script. A script is essentially a dynamic schema. That is, instead of the set of typical fixed features in a schema, a script has a series of conventional actions that take place. You have a script for “Going to the dentist” and another script for “Going to the movies.” We all have versions of an “Eating in a restaurant” script, which we can activate to make sense of this short text.

On the basis of our restaurant script, we would be able to say a number of things about the scene and events briefly described in this short text. For example, although the text doesn’t have this information, we would assume that Suzy opened a door to get into the restaurant, that there were tables there, that she ate the sandwich, then she paid for it, and so on. The fact that information of this type can turn up in people’s attempts to remember the text is further evidence of the existence of scripts. It is also a good indication of the fact that our understanding of what we read doesn’t come directly from what words and sentences are on the page, but the interpretations we create, in our minds, of what we read.
Indeed, crucial information is sometimes omitted from important instructions on the assumption that everybody knows the script. Think carefully about the following instructions from a bottle of cough syrup.
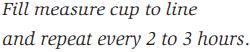
No, you’ve not just to keep filling the measure cup every 2 to 3 hours. Nor have you to rub the cough syrup on your neck or in your hair. You are expected to know the script and drink the stuff from the measure cup every 2 or 3 hours.
Clearly, our understanding of what we read is not only based on what we see on the page (language structures), but also on other things that we have in mind (knowledge structures). To understand more about the connection between these two things, we have to take a close look at the workings of the human brain.
 الاكثر قراءة في pragmatics
الاكثر قراءة في pragmatics
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















