

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Reactivity of Multiple Carbon-Carbon Bonds
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
16-1-2022
2369
The Reactivity of Multiple Carbon-Carbon Bonds
In the early days of organic chemistry, alkenes were described as "unsaturated" because, in contrast to the "saturated" alkanes, they were found to react readily with substances such as halogens, hydrogen halides, oxidizing agents, and so on. Therefore, the "chemical affinity" of alkenes was regarded as unsatisfied or "unsaturated".
One reason alkenes and alkynes react more readily than alkanes is because the carbon-carbon bonds of a multiple bond are individually weaker than normal carbon-carbon single bonds. Consider the bond energies involved. According to Table 4-3, the strengths of carbon-carbon single, double, and triple bonds are 83, 146, and 200kcal, respectively. From these values we can calculate that cleavage of one-half of a carbon-carbon double bond should require 63kcal and cleavage of one-third of a carbon-carbon triple bond should require 54kcal:

As a result, addition reactions to multiple bonds are expected to be about 20-30kcal more exothermic than the corresponding cleavage reactions of carbon-carbon single bonds, as estimated here for reaction with bromine:
The substantial difference in the heats of reaction of ethane, ethene, and ethyne with bromine is reflected in a very important practical consideration in handling ethyne (acetylene), namely its thermodynamic stability relative to solid carbon and hydrogen gas. Unlike ethane, both ethene and ethyne can be shown from bond energies to be unstable with respect to formation of solid carbon and gaseous hydrogen:
Although this does not seem to offer particular problems with ethene, an explosive decomposition of ethyne to carbon and hydrogen may occur if the gas is compressed to 10-20kg cm−2. Even liquid ethyne (bp . -83 oC) must be handled with care. Ethyne is not used commercially under pressure unless it is mixed with an inert gas and handled in rugged equipment. Ethyne burns with pure oxygen to give a very hot flame that is widely used for welding. For this purpose, the gas is dissolved under about 15kg cm−2 in 2-propanone (acetone, 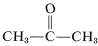 , bp 56.5o) and contained in cylinders packed with diatomaceous earth.
, bp 56.5o) and contained in cylinders packed with diatomaceous earth.
Why is ethyne so much less stable than ethene or ethane? First, C−C bonds are not as strong as C−H bonds. Therefore a gain in stability usually is to be expected when C−H bonds are made at the expense of C−C bonds; ethene and ethane each have more C−H bonds than ethyne has. Second, ethyne has six electrons held between the two carbons and these electrons experience considerable mutual interelectronic repulsion. This accounts for the fact that the average C−C bond strength for the triple bond of an alkyne is 200/3=67kcal, compared to 146/2=73kcal for the double bond of an alkene and 83kcal for a normal single bond of an alkane.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















