
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
REFLECTION
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
500
8-11-2020
2936
REFLECTION
Prehistoric people surely knew about reflection. It would not take an intelligent creature very long to figure out that the “phantom in the pond” was actually a visual image of himself or herself. Any smooth, shiny surface reflects some of the light that strikes it. If the surface is perfectly flat, perfectly shiny, and reflects all the light that strikes it, then any ray that encounters the surface is reflected away at the same angle at which it hits. You have heard the expression, “The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.” This principle, known as the law of reflection, is illustrated in Fig. 1.
In optics, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are both measured relative to a normal line (also called an orthogonal or perpendicular). In Fig.1, these angles are denoted q and can range from 0°, where the light ray strikes at a right angle with respect to the surface, to almost 90°, a grazing angle relative to the surface.
If the reflective surface is not perfectly flat, then the law of reflection still applies for each ray of light striking the surface at a specific point. In such a case, the reflection is considered with respect to a flat plane passing through the point and tangent to the surface at that point. When many parallel rays of light strike a curved or irregular reflective surface at many different points, each ray obeys the law of reflection, but the reflected rays do not all emerge parallel. In some cases they converge; in other cases they diverge. In still other cases the rays are scattered haphazardly.
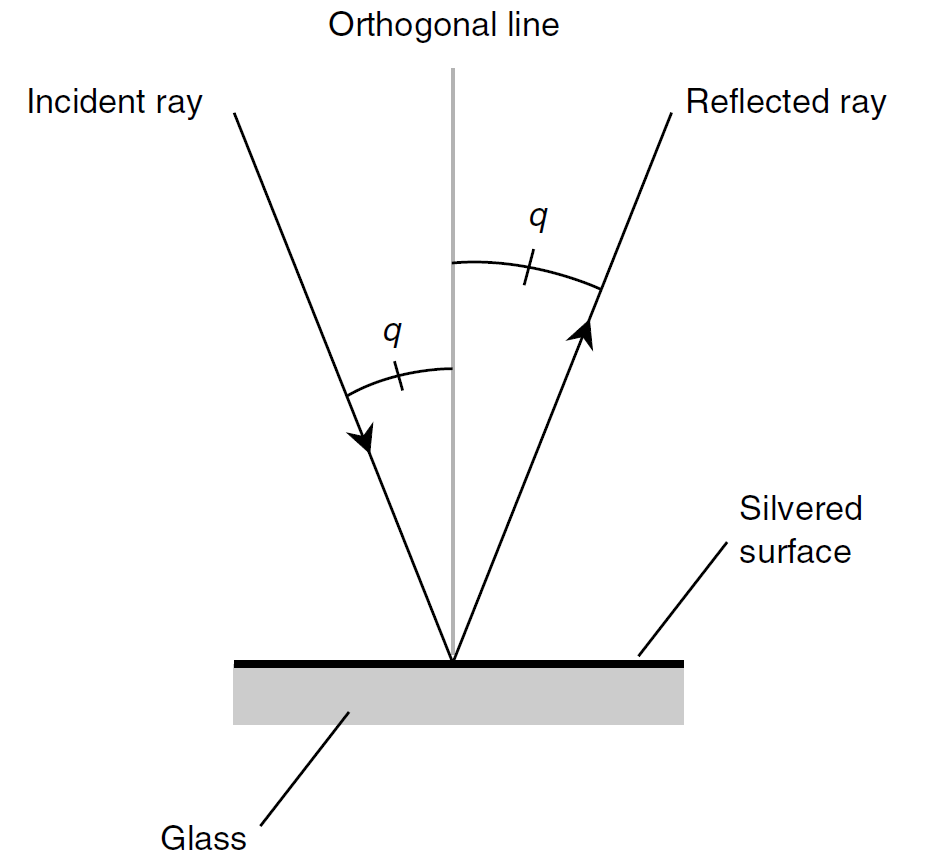
Fig. 1. When a ray of light is reflected from a shiny, flat surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Here both angles are denoted q.
 الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















