
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
KINETIC ENERGY
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
p 206
16-9-2020
2200
KINETIC ENERGY
Suppose that the object shown by the scenario in Fig. 1 is lifted a certain distance, imparting to it a potential energy Ep. What will happen if you let go of the rope, and the object falls back to the floor? First, the object might do damage, either to the floor or to itself, when it hits. Second, it will be moving, and in fact accelerating, when it hits. Third, all the potential energy that was imparted to the object in lifting it will be converted into other forms: vibration, sound, heat, and possibly the outward motion of flying chunks of concrete or linoleum.
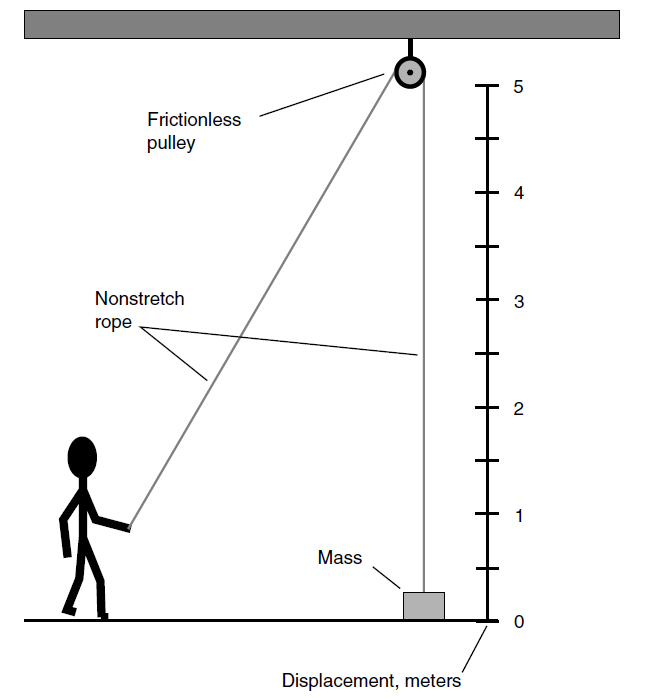
Fig. 1. Work is done when a force is applied over a specific distance. In this case, the force is applied upward to an object against Earth’s gravity.
Now think of the situation an infinitesimal moment—an instant—before the object strikes the floor. At this moment the kinetic energy possessed by the object will be just equal to the potential energy imparted to it by lifting it. All this kinetic energy is about to be dissipated or converted in the violence of impact. The kinetic energy is
Ek = Fq = magq = 9.8mq
where F is the force applied, q is the distance the object was raised (and thus the distance it falls), m is the mass of the object, and ag is the acceleration of gravity. Here we are taking ag to be 9.8 m/s2, accurate to only two significant figures.
There is another way to express Ek for a moving object having a mass m. This is
Ek = mv2/2
where v is the speed of the object just before impact. We could use the formulas for displacement, but there’s no need. We already have a formula for kinetic energy in the example of Fig. 1. The mass-velocity formula is far more general and applies to any moving object, even if work is not done on it. Another note should be made here. You will notice that we use the notation m (lowercase italic m) for mass and m (lowercase nonitalic m) for meter(s). It is easy to get careless and confuse these. Don’t.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















