
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
HOW VELOCITY IS DETERMINED
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
p 182
13-9-2020
2317
HOW VELOCITY IS DETERMINED
Velocity can be measured by using a speedometer in combination with some sort of device that indicates the instantaneous direction of travel. In a car, this might be a magnetic compass. In a strict sense, however, even a speedometer and a compass don’t tell the whole story unless you’re driving on a flat plain or prairie. In midstate South Dakota, a speedometer and compass can define the instantaneous velocity of your car, but when you get into the Black Hills, you’ll have to include a clinometer (a device for measuring the steepness of the grade you’re ascending or descending).
Two-dimensional direction components can be denoted either as compass (azimuth) bearings or as angles measured counterclockwise with respect to the axis pointing “east.” The former system is preferred by hikers and navigators, whereas the latter scheme is preferred by theoretical physicists and mathematicians. In Fig. 1, the azimuth bearings of vectors a, b, and c are approximately 90, 120, and 45 degrees, respectively. In the mathematical model, they are about 0, -30 (or 330), and 45 degrees, respectively.
A three-dimensional velocity vector consists of a magnitude component and two direction angles. Celestial latitude and longitude or right ascension and declination are used commonly to denote the directions of velocity vectors.
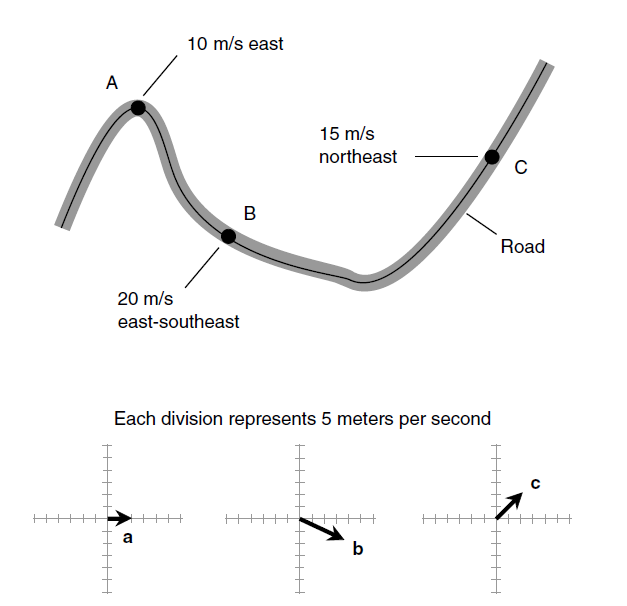
Fig. 1. Velocity vectors a, b, and c for a car at three points (A, B, and C) along a road.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















