

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Ambident Character of Enolate Anions
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
18-11-2019
1925
The Ambident Character of Enolate Anions
Since the negative charge of an enolate anion is delocalized over the alpha-carbon and the oxygen, electrophiles may bond to either atom. Reactants having two or more reactive sites are called ambident, so this term is properly applied to enolate anions. Modestly electrophilic reactants such as alkyl halides are not sufficiently reactive to combine with neutral enol tautomers, but the increased nucleophilicity of the enolate anion conjugate base permits such reactions to take place. Because alkylations are usually irreversible, their products should reflect the inherent (kinetic) reactivity of the different nucleophilic sites.
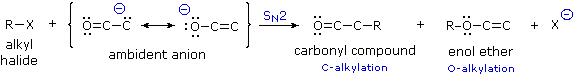
If an alkyl halide undergoes an SN2 reaction at the carbon atom of an enolate anion the product is an alkylated aldehyde or ketone. On the other hand, if the SN2 reaction occurs at oxygen the product is an ether derivative of the enol tautomer; such compounds are stable in the absence of acid and may be isolated and characterized. These alkylations (shown above) are irreversible under the conditions normally used for SN2 reactions, so the product composition should provide a measure of the relative rates of substitution at carbon versus oxygen. It has been found that this competition is sensitive to a number of factors, including negative charge density, solvation, cation coordination and product stability.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















