

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
HOMEWORK AND PRACTICE Classroom Example
المؤلف:
Jane D. Hill Kathleen M. Flynn
المصدر:
Classroom Instruction that works with English Language Learners
الجزء والصفحة:
P80-C8
2025-09-12
71
HOMEWORK AND PRACTICE Classroom Example
Subject: Social Studies
Content Objective: To recognize a variety of influences on consumers and how these influences affect decisions about purchases.
Students have already discovered that they are surrounded by images and messages telling them what to buy, what is better, what tastes better, and so forth. They have also explored the creators of these images and messages, and the audiences they are targeting. Students chose a product as a whole-class activity and then discussed and demonstrated advertisers’ claims about the product (e.g., it tastes good, improves health, is fast-acting). They also talked about how the advertisers got the audience’s attention and what factors induced the students to buy the product. They pointed out pictures or words that persuade consumers. They discussed and brought in examples of advertising from various media sources (e.g., TV, radio, billboards, flyers, signs at grocery stores, newspapers, magazines, the Internet, coupons).
After much discussion, demonstration, and classroom activities, the following homework was assigned. Students were asked to gather examples of advertising that influenced a purchase made by their mother or father or one that incited the students themselves to convince their parents to buy a product for them. The students then were asked to either draw or write a description of that experience. They were also given the choice of writing about an ad they saw on TV, heard on the radio, or saw in a magazine that was convincing, and discussing how it was convincing (e.g., message, presentation, price). The teacher was careful to set a reasonable expectation for this assignment by stating how many paragraphs were expected and by emphasizing that drawings should illustrate what was convincing about the advertisement.
Preproduction
Students can practice words for items they studied during class by finding or drawing another example from home. For example, when the class talks about Nike shoes, students learn the words “toe,” “heel,” “shoelaces,” and “swoosh.” For homework, they can draw a shoe and label the parts (see Figure 1). They can also be assigned to draw and label five items from home that have been discussed in class.
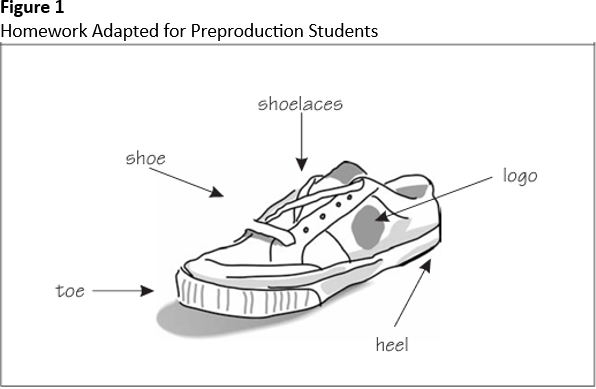
Any word selection activity you can provide will keep them in the learning loop. You can then assess vocabulary with statements such as “Show me the toe” or “Point to the shoelaces.”
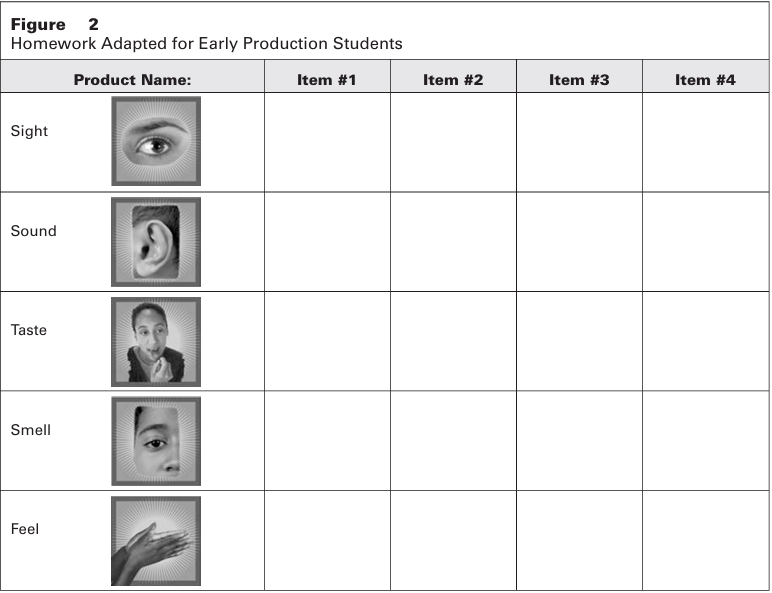
Early Production Students can also use practice with vocabulary. In addition to nouns, they should be working on vocabulary for sight, touch, sound, taste, and smell. For homework, they can select four items from home and practice writing their new vocabulary in the chart provided (see Figure 2).
Speech Emergence
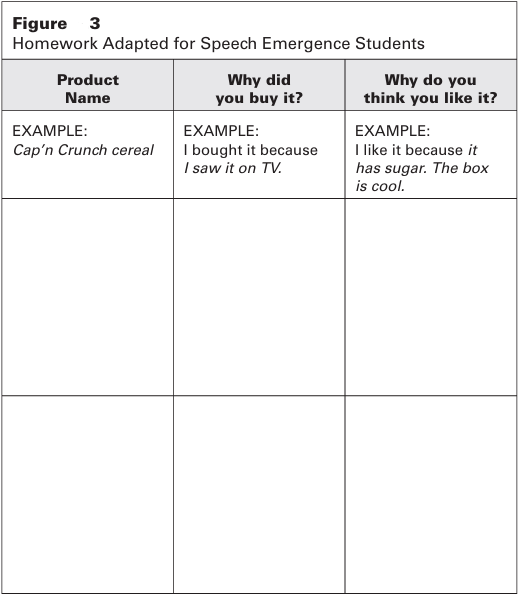
Students can select items from home and complete the chart depicted in Figure 3. The first row gives an example for students.
Intermediate and Advanced Fluency
Students can draw something they saw on TV and describe why it was convincing according to at least three criteria (e.g., message, presentation, and price).
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















