
Distinctive features
 المؤلف:
Peter Roach
المؤلف:
Peter Roach
 المصدر:
English Phonetics and Phonology A practical course
المصدر:
English Phonetics and Phonology A practical course
 الجزء والصفحة:
113-13
الجزء والصفحة:
113-13
 2024-10-31
2024-10-31
 1283
1283
Distinctive features
Many references have been made to phonology in this course, with the purpose of making use of the concepts and analytical techniques of that subject to help explain various facts about English pronunciation as efficiently as possible. One might call this "applied phonology"; however, the phonological analysis of different languages raises a great number of difficult and interesting theoretical problems, and for a long time the study of phonology "for its own sake" has been regarded as an important area of theoretical linguistics. Within this area of what could be called "pure phonology", problems are examined with little or no reference to their relevance to the language learner. Many different theoretical approaches have been developed, and no area of phonology has been free from critical examination. The very fundamental notion of the phoneme, for example, has been treated in many different ways. One approach that has been given a lot of importance is distinctive feature analysis, which is based on the principle that phonemes should be regarded not as independent and indivisible units, but instead as combinations of different features. For example, if we consider the English d phoneme, it is easy to show that it differs from the plosives b, g in its place of articulation (alveolar), from t in being lenis, from s, z in not being fricative, from n in not being nasal, and so on. If we look at each of the consonants just mentioned and see which of the features each one has, we get a table like this, where + means that a phoneme does possess that feature and - means that it does not.
If you look carefully at this table, you will see that the combination of + and - values for each phoneme is different; if two sounds were represented by exactly the same +'s and -'s, then by definition they could not be different phonemes.
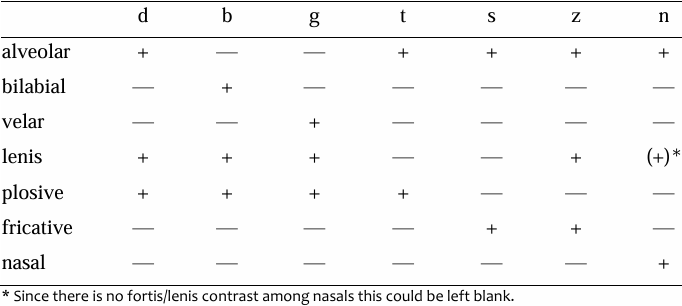
In the case of the limited set of phonemes used for this example, not all the features are needed: if one wished, it would be possible to dispense with, for example, the feature velar and the feature nasal. The g phoneme would still be distinguished from b, d by being neither bilabial nor alveolar, and n would be distinct from plosives and fricatives simply by being neither plosive nor fricative. To produce a complete analysis of all the phonemes of English, other features would be needed for representing other types of consonant, and for vowels and diphthongs. In distinctive feature analysis the features themselves thus become important components of the phonology.
It has been claimed by some writers that distinctive feature analysis is relevant to the study of language learning, and that pronunciation difficulties experienced by learners are better seen as due to the need to learn a particular feature or combination of features than as the absence of particular phonemes. For example, English speakers learning French or German have to learn to produce front rounded vowels. In English it is not necessary to deal with vowels which are +front, +round, whereas this is necessary for French and German; it could be said that the major task for the English-speaking learner of French or German in this case is to learn the combination of these features, rather than to learn the individual vowels y, Ø and (in French) œ1.
English, on the other hand, has to be able to distinguish dental from labiodental and alveolar places of articulation, for θ to be distinct from f, s and for ð to be distinct from v, z. This requires an additional feature that most languages do not make use of, and learning this could be seen as a specific task for the learner of English. Distinctive feature phonologists have also claimed that when children are learning their first language, they acquire features rather than individual phonemes.
1 The phonetic symbols represent the following sounds: y is a close front rounded vowel (e.g. the vowel in French tu, German Bühne); 0 is a close-mid front rounded vowel (e.g. French peu, German schön); œ is an open-mid front rounded vowel (e.g. French oeuf).
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics and Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics and Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


