

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Research and data
المؤلف:
Gunnel Melchers
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
38-2
2024-02-10
1292
Research and data
There exists as yet no definitive description of the present-day phonology of the Northern Isles. A number of young scholars, however, are currently researching topics such as the Shetland vowel system, aspects of quantity in Orkney and Shetland speech, and dialect levelling in young speakers. The final results from this research, which tends to focus on realizations of Standard (Scottish) English rather than traditional dialect, are unfortunately not yet available at the time of writing this text.
The only existing full-length work on Orkney dialect as spoken in the 20th century is Marwick’s The Orkney Norn (1929). Confusingly, Marwick uses the term Norn both for the all-Scandinavian language once spoken on the islands and for contemporary Orkney dialect. His work is mainly a dictionary of the dialect but with a brief introduction to grammar and phonology and with phonetic transcriptions of all headwords. As the title suggests, it has a marked Scandinavian and historical bias, particularly apparent in the phonology, which takes the Old Norse sound system as its starting-point, simply listing its modern reflections in Orkney. Although contemporary evidence suggests that Marwick’s data are characterized by a touch of “Nornomania” and that he had preconceived notions of “correct” answers from his informants, his work is clearly of great importance for the present study. As a phonetician he seems very competent, and fairly narrow distinctions, such as [o] vs. 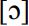 have been noted in individual entries.
have been noted in individual entries.
Shetland dialect as spoken at the end of the 19th century was carefully documented in the Faroese scholar Jakob Jakobsen’s monumental An Etymological Dictionary of the Norn Language in Shetland (1928–1932). As the title suggests, it, too, has a clear Scandinavian bias but provides information about the language variety as a whole, including phonology (pre-structural, naturally). Jakobsen, who was a trained philologist in the German school, notes very fine distinctions indeed, to the degree that he has been accused of practising “phonetics run riot” (cf. Waugh 1996: 6). Some of his headwords have up to twenty-five different realizations, but there is no indication of a systematic account of vowels and consonants. This does not mean that he should be ignored in a study of Shetland phonology.
The phonological section of The Linguistic Survey of Scotland (LSS) (cf. Mather and Speitel 1986), which above all was designed to elicit vowel systems, included a number of localities in the Northern Isles (thirteen in Orkney, ten in Shetland). John C. Catford, who was instrumental in setting up the survey, took the view that Shetland phonology was unique among Scottish accents in its rich vowel system, palatalization of final /d/, /n/, and /l/, certain consonant mergers and characteristic syllable structure. Before the actual launching of the LSS, Catford found it necessary to do some pilot fieldwork in Shetland, “a phonological reconnaissance”, which resulted in a special Shetland section in the questionnaire, e.g. eliciting Scandinavian-based words expected to be realized with [ø], such as brööl ‘moo’. There was no similar highlighting of Orkney. Catford (1957: 75) assesses Shetland dialect in general as having a “somewhat archaic character”, suggesting that its vowel system may be similar to Scots as spoken in the metropolitan area of Scotland in the 16th–17th centuries. Interestingly, aspects of Shetland verbal usage can also be characterized as archaic (cf. Melchers, other volume).
A recent excellent study of Insular Scots, i.e. Orcadian and ‘Shetlandic’, based on data from LSS and considering Catford’s preliminary analyses of vowel systems, can be extracted from Paul Johnston’s chapter on regional variation for the Edinburgh History of the Scots Language (Johnston 1997).
The only existing account of a particular Insular Scots accent is Elise Orten’s The Kirkwall Accent (Orten 1991), an M.A. thesis submitted at the University of Bergen, claiming to be “based on the London School of phonology”, but not making use of the Wells lexical sets.
An interesting source of information is John Tait’s article on Shetland vowels (Tait 2000). Tait, a native Shetlander, first began taking an interest in Shetland phonology for the purpose of creating a workable writing system. He takes a critical view of the LSS material and introduces the concept of “soft mutation”, i.e. the raising of certain vowels before certain consonants, which “provides, along with vowel length, a framework for looking at Shetlandic vowel phonology as a whole”.
With the help of instrumental analysis, van Leyden (2002) has investigated vowel and consonant duration in Orkney and Shetland dialects, taking Catford’s impressionistic observations as her starting-point. Whereas her Shetland data suggested a Scandinavian-like pattern, Orkney showed more affinity with Standard Scottish English.
In addition to the research described above, this presentation draws on material collected for a project entitled The Scandinavian Element in Shetland Dialect, directed by the present writer. The material consists of tape-recordings eliciting phonological as well as lexical and attitudinal aspects. In addition, a great deal of material recorded for the purpose of oral history has been placed at my disposal by the Orkney and Shetland Archives. This is particularly useful since the interviewers are mostly dialect speakers themselves, which means that the informants do not tend to adapt their language.
For the purpose of this publication, recordings were made in Shetland and Orkney during the summer of 2002. Regrettably, however, the presentation will still have a marked “Shetland bias”, since considerably more data and information is available on the most northerly part of the Insular Scots region.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















