


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-1-2018
Date: 24-6-2019
Date: 11-2-2016
|
Major uses of the group 2 metals and their compounds
Beryllium is one of the lightest metals known, is nonmagnetic, and has a high thermal conductivity and a very high melting point (1560 K); these properties, combined with inertness towards aerial oxidation, render it of industrial importance. It is used in the manufacture of body parts in high-speed aircraft and missiles, and in communication satellites. Because of its low electron density, Be is a poor absorber of electromagnetic radiation and, as a result, is used in X-ray tube windows. Its high melting point and low cross-section for neutron capture make Be useful in the nuclear energy industry. Figure 1.1 summarizes the major uses of Mg.
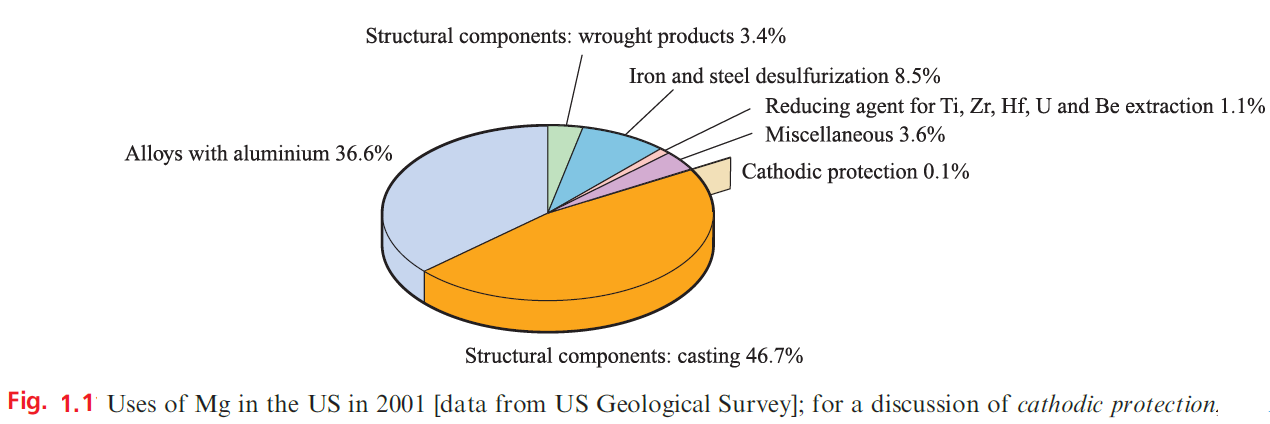
The presence of Mg in Mg/Al alloys imparts greater mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion, and improves fabrication properties; Mg/Al alloys are used in aircraft and automobile body parts and lightweight tools. Miscellaneous uses include flares, fireworks and photographic flashlights, and medical applications such as indigestion powders (milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2) and a purgative (Epsom salts, MgSO4.7H2O). Both Mg2 +and Ca2+ ions are catalysts for diphosphate–triphosphate transformations in biological systems; Mg2+ is an essential constituent of chlorophylls in green plants.
Uses of compounds of calcium far outnumber those of the metal, with the world production of CaO, Ca(OH)2, CaO.MgO, Ca(OH)2.MgO and Ca(OH)2.Mg(OH)2 being 118 000Mt in 2000. Calcium oxide (quicklime or lime) is produced by calcining limestone and a major use is as a component in building mortar. Dry sand and CaO mixtures can be stored and transported; on adding water, and as CO2 is absorbed, the mortar sets as solid CaCO3 .The sand in themortar is a binding agent.
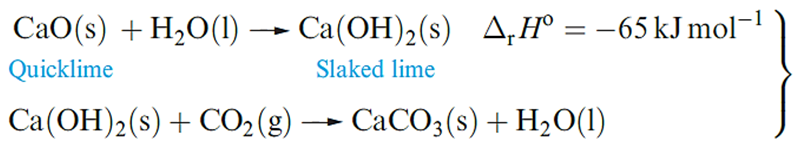
Other important uses of lime are in the steel industry (see Box 5.1), pulp and paper manufacturing, and extraction of Mg. Calcium carbonate is in huge demand in, for example, steel, glass, cement and concrete manufacturing, and the Solvay process.
Recent applications of CaCO3 and Ca(OH)2 with environmental significance are in desulfurization processes. Large quantities of Ca(OH)2 are used to manufacture bleaching powder, Ca(OCl)2.Ca(OH)2.CaCl2.2H2O and in water treatment.
Calcium fluoride occurs naturally as the mineral fluorspar, and is commercially important as the raw material for the manufacture of H and F2. Smaller amounts of CaF2 are used as a flux in the steel industry, for welding electrode coatings, and in glass manufacture; prisms and cell windows made from CaF2 are used in spectrophotometers.
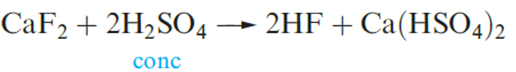
The two mineral sources for strontium are the sulfate (celestite) and carbonate (strontianite). In 2001, 75% of strontium used in the US went into the manufacture of faceplate glass in colour television cathode-ray tubes in order to stop X-ray emissions. It is present as SrO and has the added advantage of enhancing television picture quality. Other uses of strontium include ferrite ceramic magnets and pyrotechnics. Barite (or barytes) is the mineral form of BaSO4. World production in 2001 was ≈ 6600 Mt, with Chile supplying over half this total. The major use of barite is as a weighting material in oil- and gas-well drilling fluids. On a much smaller scale of application, the ability of BaSO4 to stop the passage of X-rays leads to its use as a ‘barium meal’ in radiology for imaging the alimentary tract. Uses of Ba as a ‘getter’ in vacuum tubes arise from its high reactivity with gases including O2 and N2.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|