
METATHESIS OF OLEFINS
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 246
الجزء والصفحة:
p 246
 3-9-2017
3-9-2017
 1589
1589
METATHESIS OF OLEFINS
Metathesis is a catalyzed reaction that converts two olefin molecules into two different olefins. It is an important reaction for which many mechanistic approaches have been proposed by scientists working in the fields of homogenous catalysis and polymerization. One approach is the formation of a fluxional five-membered metallocycle. The intermediate can give back the starting material or the metathetic products via a concerted mechanism:
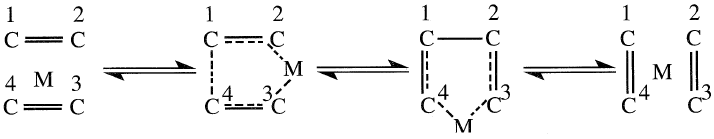
Another approach is a stepwise mechanism that involves the initial formation of a metal carbene followed by the formation of a four-membered metallocycle species:
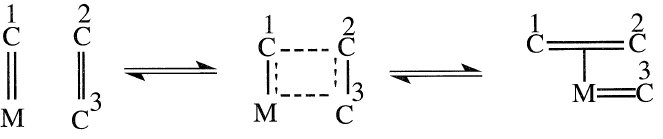
Olefin metatheses are equilibrium reactions among the two-reactant and two-product olefin molecules. If chemists design the reaction so that one product is ethylene, for example, they can shift the equilibrium by removing it from the reaction medium. Because of the statistical nature of the metathesis reaction, the equilibrium is essentially a function of the ratio of the reactants and the temperature. For an equimolar mixture of ethylene and 2-butene at 350°C, the maximum conversion to propylene is 63%. Higher conversions require recycling unreacted butenes after fractionation. This reaction was first used to produce 2-butene and ethylene from propylene. The reverse reaction is used to prepare polymer-grade propylene form 2-butene and ethylene:
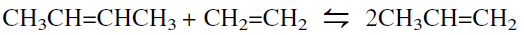
The metathetic reaction occurs in the gas phase at relatively high temperatures (150°–350°C) with molybdenum or tungsten supported catalysts or at low temperature (≈50°C) with rhenium-based catalyst in either liquid or gas-phase. The liquid-phase process gives a better conversion.
Equilibrium conversion in the range of 55–65% could be realized, depending on the reaction temperature.8 In this process, which has been jointly developed by Institute Francais du Petrole and Chinese Petroleum Corp., the C4 feed is mainly composed of 2-butene (1-butene does not favor this reaction but reacts differently with olefins, producing metathetic by-products). The reaction between 1- butene and 2-butene, for example, produces 2-pentene and propylene.
The amount of 2-pentene depends on the ratio of 1-butene in the feedstock. 3-Hexene is also a by-product from the reaction of two butane molecules (ethylene is also formed during this reaction). The properties of the feed to metathesis are shown in Table 1-1. Table 1-2 illustrates the results from the metatheses reaction at two different conversions. The main by-product was 2-pentene. Olefins in the range of C6–C8 and higher were present, but to a much lower extent than C5.
Figure 1.1 shows a simplified flow diagram for the olefin metathesis.
Table 1-1: Properties of feed to the metathesis process

Table 1-2: Results of metathesis of 2-butene at two conversion levels
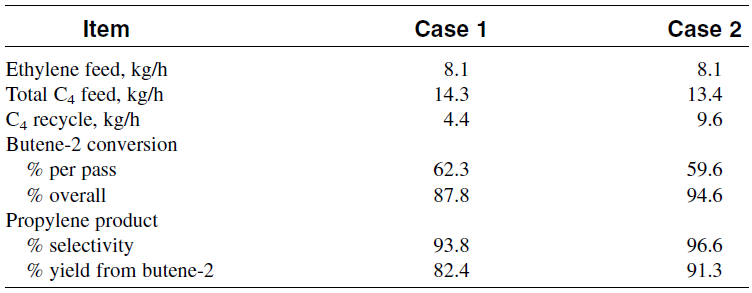
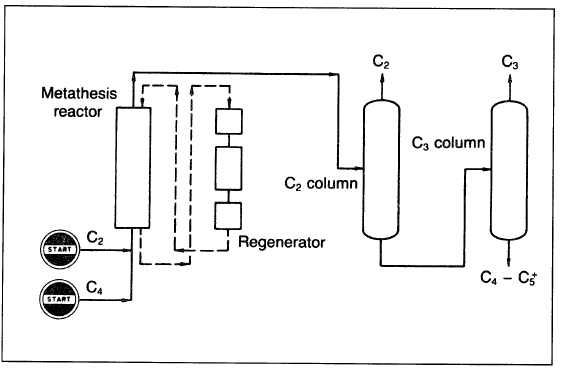
Figure 1.1. A flow diagram showing the metathesis process for producing polymer grade propylene from ethylene and 2-butene.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


