

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Reforming Process
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 68
24-7-2017
1643
Reforming Process
Catalytic reformers are normally designed to have a series of catalyst beds (typically three beds). The first bed usually contains less catalyst than the other beds. This arrangement is important because the dehydrogenation of naphthenes to aromatics can reach equilibrium faster than the other reforming reactions. Dehydrocyclization is a slower reaction and may only reach equilibrium at the exit of the third reactor. Isomerization and hydrocracking reactions are slow. They have low equilibrium constants and may not reach equilibrium before exiting the reactor.
The second and third reactors contain more catalyst than the first one to enhance the slow reactions and allow more time in favor of a higher yield of aromatics and branched paraffins. Because the dehydrogenation of naphthenes and the dehydrocyclization of paraffins are highly endothermic, the reactor outlet temperature is lower than the inlet temperature. The effluent from the first and second reactors are reheated to compensate for the heat loss.
Normally, catalytic reformers operate at approximately 500–525°C and 100–300 psig, and a liquid hourly space velocity range of 2–4 hr-1. Liquid hourly space velocity (LHSV) is an important operation parameter expressed as the volume of hydrocarbon feed per hour per unit volume of the catalyst. Operating at lower LHSV gives the feed more
contact with the catalyst.
Regeneration of the catalyst may be continuous for certain processes that are designed to permit the removal and replacement of the catalyst during operation. In certain other processes, an additional reactor is used (Swing reactor). When the activity of the catalyst is decreased in one of the reactors on stream, it is replaced with the stand-by (Swing) reactor.
In many processes, regeneration occurs by shutting down the unit and regenerating the catalyst (Semi-regenerative). Figure 1.1 shows a Chevron Rheiniforming semiregenerative fixed three-bed process.
Products from catalytic reformers (the reformate) is a mixture aromatics, paraffins and cycloparaffins ranging from C6-C8. The mixture has a high octane rating due to presence of a high percentage of aromatics and branched paraffins. Extraction of the mixture with a suitable solvent produces an aromatic-rich extract, which is further fractionated to separate the BTX components. Extraction and extractive distillation of reformate have been reviewed by Gentray and Kumar.
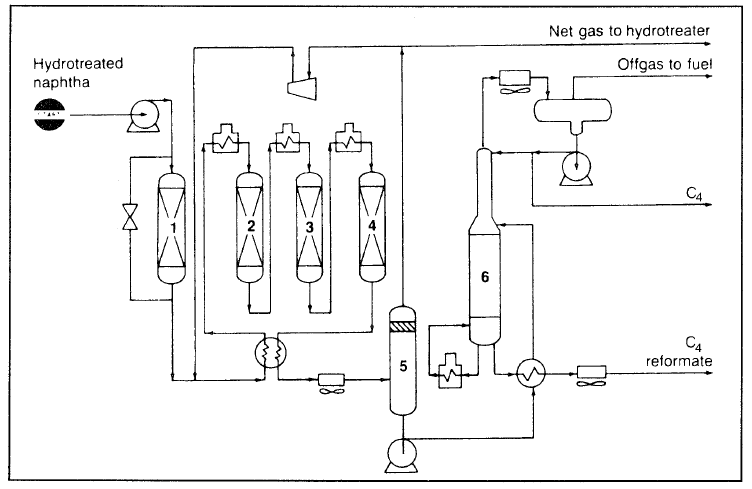
Figure 1.1. Flow diagram of a Chevron Rheiniforming unit: (1) sulfur sorber, (2–4) reactors, (5) separator, (6) stabilizer.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















