
Wave-Particle Duality
 المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
 المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 26
الجزء والصفحة:
p 26
 13-5-2017
13-5-2017
 2068
2068
Wave-Particle Duality
We have seen in the last section that light waves, in the photoelectric effect, behave as if they are particles. The particle-like behavior of electromagnetic waves was also instrumental in the explanation of the Compton effect. In this experiment, an x-ray beam was incident on a solid. A portion of the x-ray beam was deflected and the frequency of the deflected wave had shifted compared to the incident wave. The observed change in frequency and the deflected angle corresponded exactly to the expected results of a "billiard ball" collision between an x-ray quanta, or photon, and an electron in which both energy and momentum are conserved.
In 1924. de Broglie postulated the existence of matter waves. He suggested that since waves exhibit particle-like behavior, then panicles should be expected to show wave-like properties. The hypothesis of de Broglie was the existence of a
wave-particle duality principle. The momentum of a photon is given by
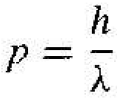 (1)
(1)
where λ is the wavelength of the light wave Then, de Broglie hypothesized that the wavelength of a particle can be expressed as
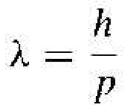 (2)
(2)
where p is the momentum of the particle and A is known as the de Broglie wavelength of the matter wave.
The wave nature of electrons has been tested in several ways. In one experiment by Davisson and Germer in 1927, electrons from a heated filament were accelerated at normal incidence onto a single crystal of nickel. A detector measured the scattered electrons as a function of angle. Figure 1.1 shows the experimental setup and Figure 1.2 shows the results. The existence of a peak in the density of scattered electrons can be explained as a constructive interference of waves scattered by the periodic atoms in the planes of the nickel crystal. The angular distribution is very similar to an interference pattern produced by light diffracted from a grating.
In order to gain some appreciation of the frequencies and wavelengths involved in the wave-particle duality principle. Figure 1.3 shows the electromagnetic frequency spectrum. We see that a wavelength of 72.7 A obtained in the next example is in the ultraviolet range. Typically, we will be considering wavelengths in the
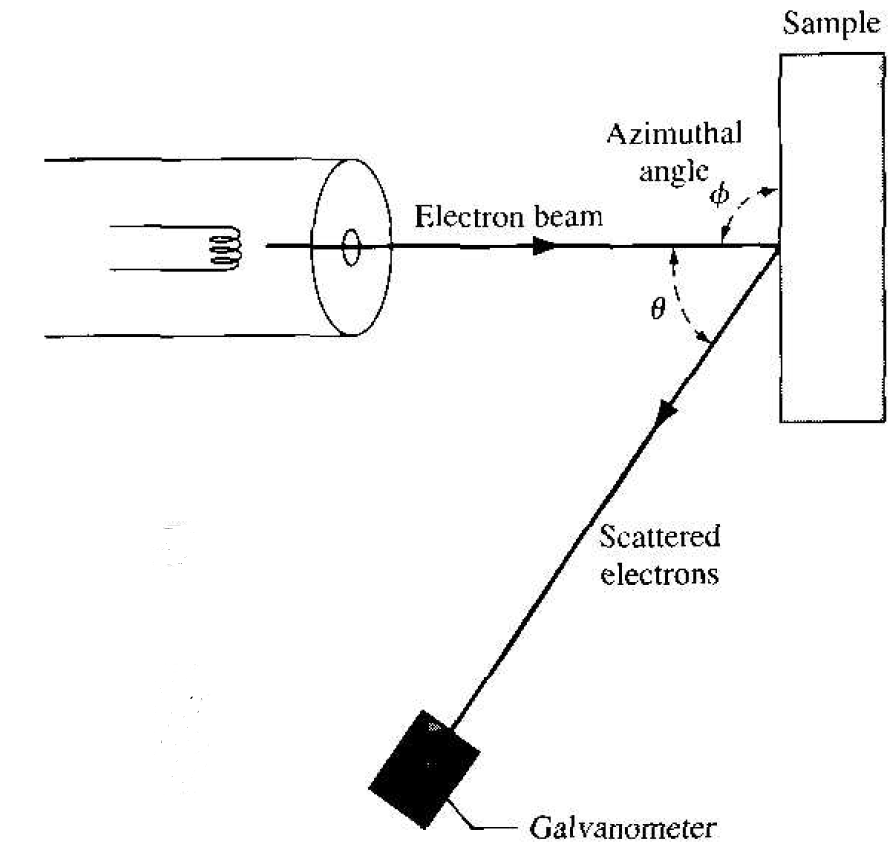
Figure 1.1 Experimental arrangement of the Davisson-Germer experiment.
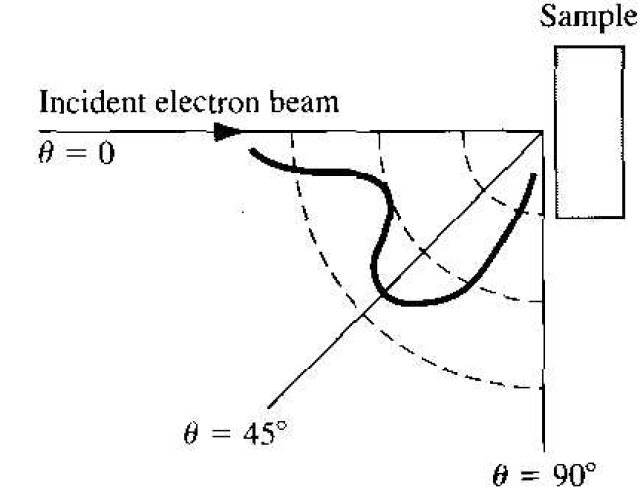
Figure 1.2 Scattered electron flux as a function of scattering angle for the Davisson-Germer experiment.
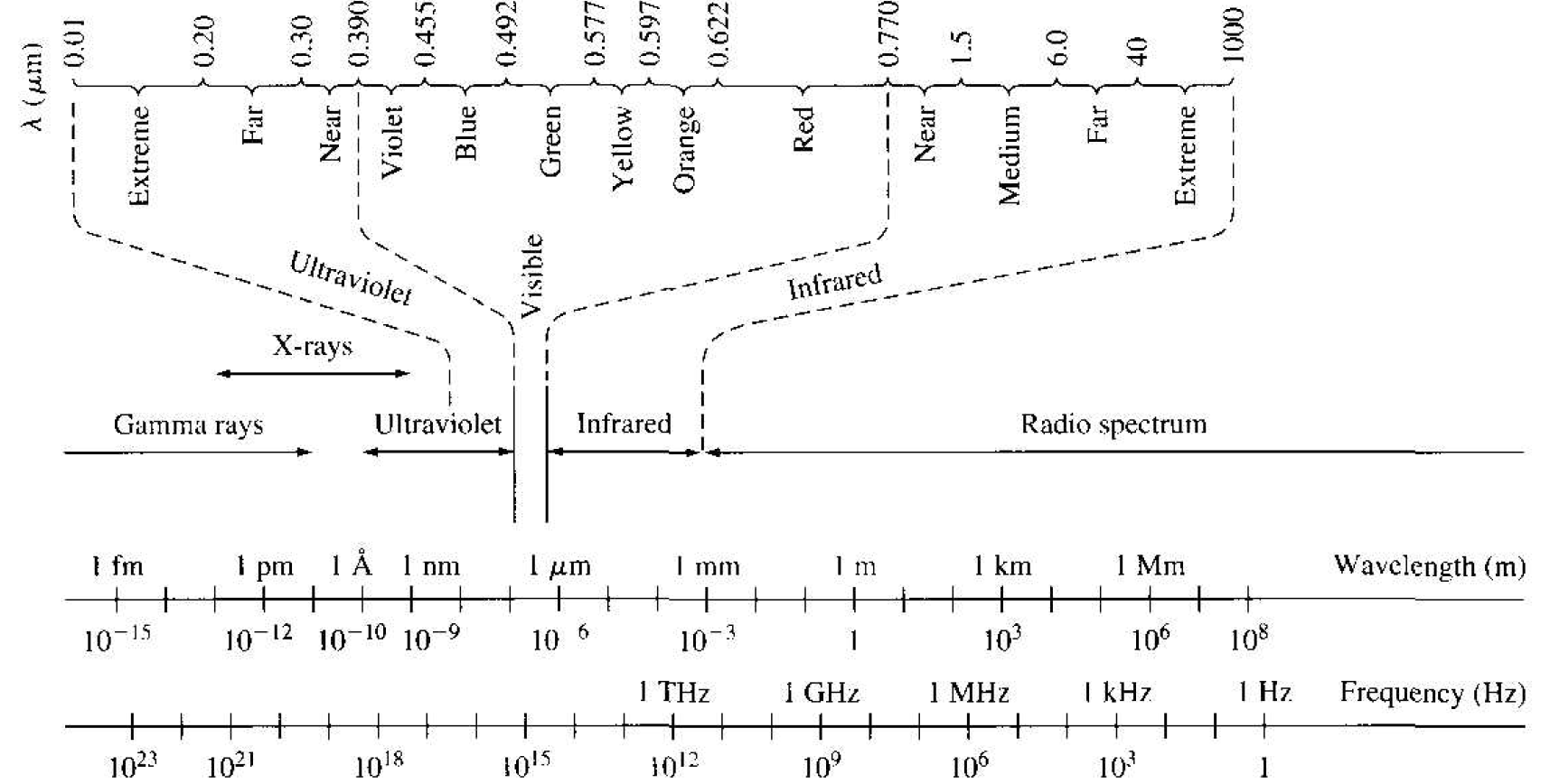
Figure 1.3 The electromagnetic frequency spectrum.
ultraviolet and visible range. These wavelengths are very short compared to the usual radio spectrum range.
In some cases electromagnetic waves behave as if they are particles (photons) and sometimes particles behave as if they are waves. This wave-particle duality principle of quantum mechanics applies primarily to small particles such as electrons, but it has also been shown to apply to protons and neutrons. For very large particles, we can show that the relevant equations reduce to those of classical mechanics. The wave-particle duality principle is the basis on which we will use wave theory to describe the motion and behavior of electrons in a crystal.
 الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


