

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
DECOMPOSITION AND SPECIAL GRAPHS
المؤلف:
Douglas B. West
المصدر:
Introduction to Graph Theory Second Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
8-10
2-8-2016
2398
The example 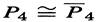 suggests a family of graph problems.
suggests a family of graph problems.
1.1. Definition.
A graph is self-complementary if it is isomorphic to its complement. A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that
each edge appears in exactly one subgraph in the list.
An n-vertex graph H is self-complementary if and only if Kn has a decomposition consisting of two copies of H.
1.2 Example.
We can decompose K5 into two 5-cycles, and thus the 5-cycle is self-complementary. Any n-vertex graph and its complement decompose Kn.
Also Kl,n-l and Kn-l. decompose Kn, even though one of these subgraphs omits a vertex. On the right below we show a decomposition of K4
using three copies consider graph decompositions. .
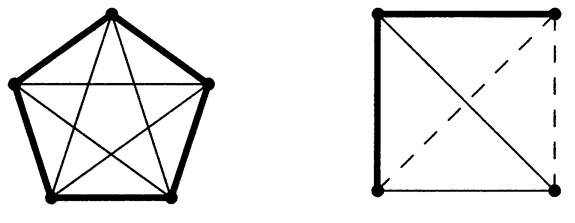
1.3 Example.
The question of which complete graphs decompose into copies of K3 is a fundamental question in the theory of combinatorial designs.
On the left below we suggest such a decomposition for K7. Rotating the triangle through seven positions uses each edge exactly once.
On the right we suggest a decomposition of K6 into copies of P4. Placing one vertex in the center groups the edges into three types: the outer 5-cycle, the inner (crossing) 5-cycle on those vertices, and the edges involving the central vertex. Each 4-vertex path in the decomposition uses one edge of each type; we rotate the picture to get the next path.
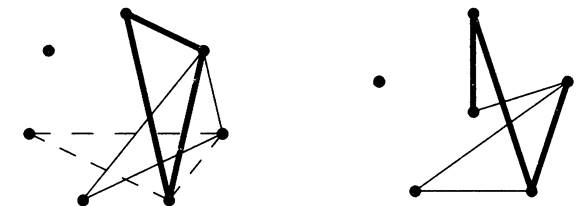
We referred to a copy of K3 as a triangle. Short names for graphs that arise frequently in structural discussions can be convenient.
1.4. Definition.
The Petersen graph is the simple graph whose vertices are the 2-element subsets of a 5-element set and whose edges are the pairs
of disjoint 2-element subsets.

We have drawn the Petersen graph in three ways above. It is a useful example so often that an entire book was devoted to it (Holton-Sheell an [I993]).
Its properties follow from the statement of its adjacency relation that we have used as the definition.
1.5. Proposition.
If two vertices are nonadjacent in the Petersen graph, then they have exactly one common neighbor.
proof.
Non adjacent vertices are 2-sets sharing one element; their union S has size 3. A vertex adjacent to both IS a 2-set disjoint from both. Since the 2-sets
are chosen from {1, 2, 3,4, 5}, there is exactly one 2-set disjoint from S.
1.6 Definition.
The girth of a graph with a cycle is the length of its shortest cycle. A graph with no cycle has infinite girth.
1.7 Definition.
An automorphism of G is an isomorphism from G to G. A graph G is vertex-transitive if for every pair u, v ϵ V (G) there is an automorphism that maps u to v.
The automorphisms of G are the permutations of V (G) that can be applied to both the rows and the columns of A(G) without changing A(G).
Introduction to Graph Theory Second Edition, Douglas B. West , Indian Reprint, 2002,page(8.10)
 الاكثر قراءة في نظرية البيان
الاكثر قراءة في نظرية البيان
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















