
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Internal and external fields
المؤلف:
J. M. D. COEY
المصدر:
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
الجزء والصفحة:
38
12-2-2021
1988
Internal and external fields
The external field H', acting on a sample that is produced by steady electric currents or the stray field of magnets outside the sample volume, is often called the applied field. The sample itself makes no contribution to H'. The internal field in the sample in our continuous medium approximation is the sum of the external field H' and the demagnetizing field Hd produced by the magnetization distribution of the sample itself:
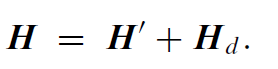 .........(1)
.........(1)
So far we have been considering the magnetization M of the material as rigid and uniform, essentially independent of the demagnetizing field. This is justified only for highly anisotropic permanent magnets having rectangular M(H) hysteresis loops for which the coercivity Hc > Hd . More generally, magnetization is induced or modified by the externally applied field H'. The internal field in the magnet H(r) depends, in turn, on the magnetization M(r). Easiest to interpret are measurements of M(H) carried out in closed magnetic circuits, where the demagnetizing field is absent. An example is the toroid of Fig. 1(a) where N = 0 and the field is that of a long solenoid H = nI. An alternative is to use a long bar or a thin film, and apply the field in the direction where N ≈ 0. If it is inconvenient to produce the sample in one of these forms, the best solution is to make it into a sphere for which the magnetization is uniform and the demagnetizing factor N = 1/3 is precisely known. Failing this, a cylindrical or block shape is used that can be approximately assimilated to an ellipsoid, and the applied field is corrected by the appropriate demagnetizing factor to obtain the internal field
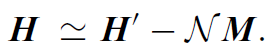 .....(2)
.....(2)
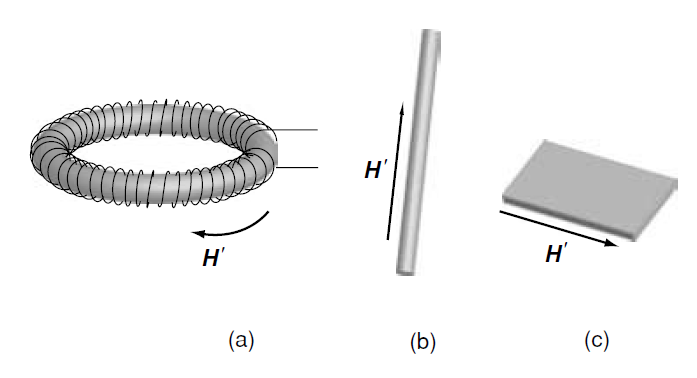
Figure 1: Ways of measuring magnetization with no need for a demagnetizing correction: (a) a toroid, (b) a long rod and (c) a thin plate.
The approximation is double: H is not uniform because the sample is not an ellipsoid, consequently M cannot be uniform either (Fig. 2).
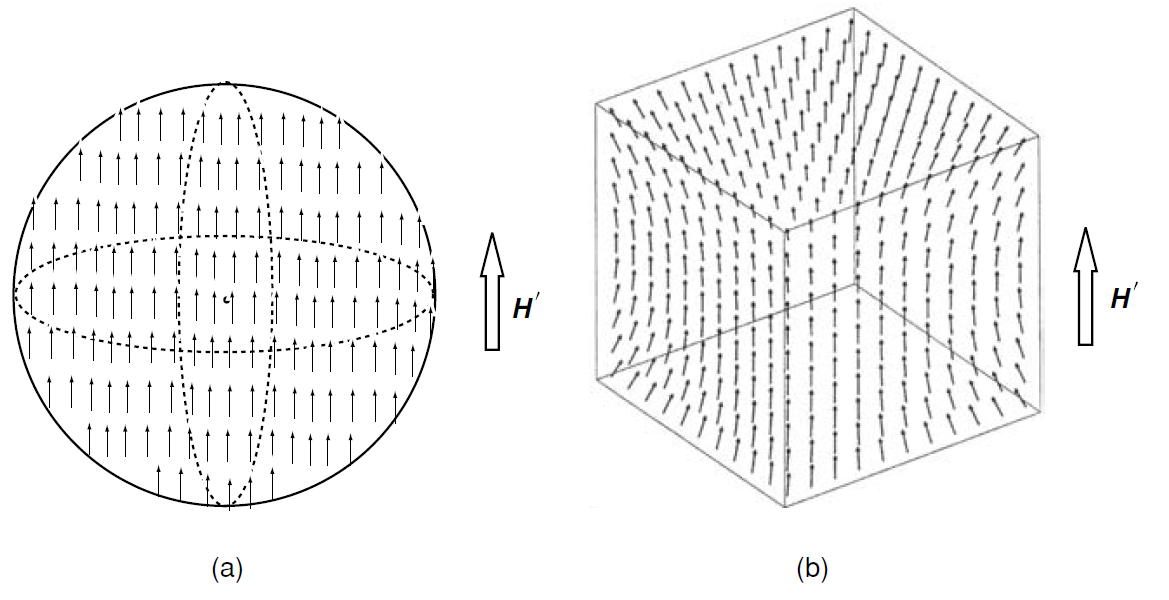
Figure 2.Magnetization of (a) a ferromagnetic sphere and (b) a ferromagnetic cube in an applied field.
A common form of sample is a powder composed of irregularly shaped but roughly spherical particles. The demagnetizing field Hd (r) then fluctuates rapidly on the scale of the particle size. When the particles pack isotropically with a packing fraction f into a sample holder having a shape with a demagnetizing factor N, the effective demagnetizing factor for the powder sample is
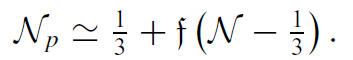 .......(3)
.......(3)
Spatial fluctuations in Hd appear near protrusions and surface irregularities. The magnetization curves and hysteresis loops measured for any of these lessthan- ideal shapes will evidently deviate from those determined for a fully dense, smooth toroid or sphere.
 الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















