

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
5-7-2019
2352
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon
The opposite of chiral is achiral. Achiral objects are superimposable with their mirror images. For example, two pieces of paper are achiral. In contrast, chiral molecules, like our hands, are non superimposable mirror images of each other. Try to line up your left hand perfectly with your right hand, so that the palms are both facing in the same directions. Spend about a minute doing this. Do you see that they cannot line up exactly? The same thing applies to some molecules
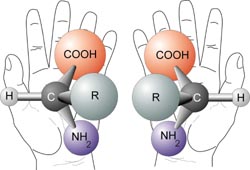
A Chiral molecule has a mirror image that cannot line up with it perfectly- the mirror images are non superimposable. The mirror images are called enantiomers. But why are chiral molecules so interesting? A chiral molecule and its enantiomer have the same chemical and physical properties(boiling point, melting point,polarity, density etc...). It turns out that many of our biological molecules such as our DNA, amino acids and sugars, are chiral molecules.
It is pretty interesting that our hands seem to serve the same purpose but most people are only able to use one of their hands to write. Similarily this is true with chiral biological molecules and interactions. Just like your left hand will not fit properly in your right glove, one of the enantiomers of a molecule may not work the same way in your body.
This must mean that enantiomers have properties that make them unique to their mirror images. One of these properties is that they cannot have a plane of symmetry or an internal mirror plane. So, a chiral molecule cannot be divided in two mirror image halves. Another property of chiral molecules is optical activity.
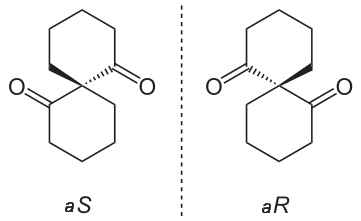
Organic compounds, molecules created around a chain of carbon atom (more commonly known as carbon backbone), play an essential role in the chemistry of life. These molecules derive their importance from the energy they carry, mainly in a form of potential energy between atomic molecules. Since such potential force can be widely affected due to changes in atomic placement, it is important to understand the concept of an isomer, a molecule sharing same atomic make up as another but differing in structural arrangements. This article will be devoted to a specific isomers called stereoisomers and its property of chirality (Figure 1.1).
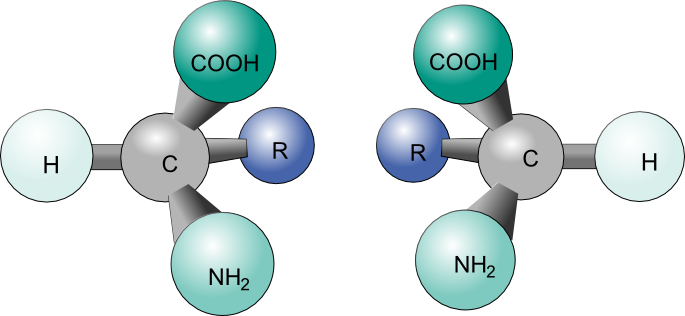
Figure 1.1. Two enantiomers of a tetrahedral complex.
The concepts of steroisomerism and chirality command great deal of importance in modern organic chemistry, as these ideas helps to understand the physical and theoretical reasons behind the formation and structures of numerous organic molecules, the main reason behind the energy embedded in these essential chemicals. In contrast to more well-known constitutional isomerism, which develops isotopic compounds simply by different atomic connectivity, stereoisomerism generally maintains equal atomic connections and orders of building blocks as well as having same numbers of atoms and types of elements.
What, then, makes stereoisomers so unique? To answer this question, the learner must be able to think and imagine in not just two-dimensional images, but also three-dimensional space. This is due to the fact that stereoisomers are isomers because their atoms are different from others in terms of spatial arrangement.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















