

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Salts of oxoacids of group 2 metal
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 286
21-1-2018
2082
Salts of oxoacids of group 2 metal
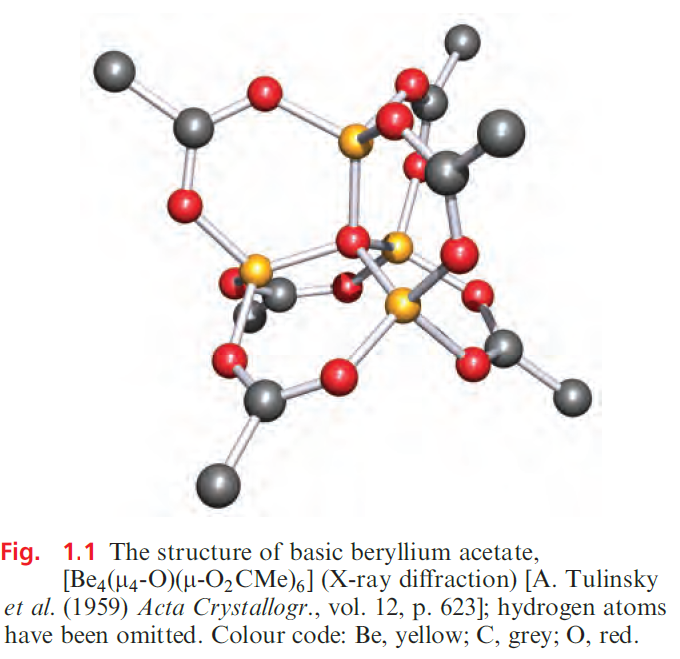
In this section, we give selected coverage of group 2 metal salts of oxoacids, paying attention only to compounds of special interest or importance. Most beryllium salts of strong oxoacids crystallize as soluble hydrates. Beryllium carbonate tends to hydrolyse, giving a salt containing [Be(H2O)4]2+. BeCO3 can be isolated only by precipitation under an atmosphere of CO2. This tendency towards hydrolysis is also illustrated by the formation of basic beryllium acetate [Be4(µ4-O) (µ -O2CMe)6] (rather than Be(MeCO2)2) by the action of MeCO2H on Be(OH)2. Figure 1.1 shows the structure of [Be4(µ4-O)(µ-O2CMe)6]; the central oxygen atom is bonded to four Be centres, each of which is tetrahedrally sited. A similar structure is observed in the basic nitrate [Be4(µ4-O) (µ-O2NO)6].

The carbonates of Mg and the later metals are sparingly soluble in water; their thermal stabilities increase with cation size, and this trend can be rationalized in terms of lattice energies. The metal carbonates are much more soluble in a solution of CO2 than in water due to the formation of [HCO3]-. However, salts of the type ‘M(HCO3)2’ have not been isolated. Hard water contains Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions which complex with the stearate ions in soaps, producing insoluble ‘scum’ in household baths and basins. Temporary hardness is due to the presence of hydrogencarbonate salts and can be overcome by boiling (which shifts equilibrium to the right-hand side causing CaCO3, or similarly MgCO3, to precipitate) or by adding an appropriate amount of Ca(OH)2.
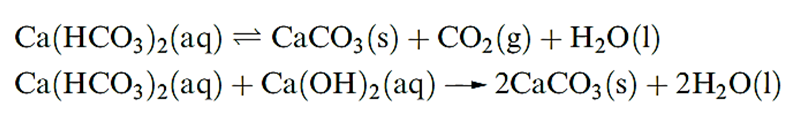
Permanent hardness is caused by other Mg2+ and Ca2+ salts (e.g. sulfates). The process of water softening involves passing the hard water through a cation-exchange resin. Washing-machine detergents contain ‘builders’ that remove Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions from washing water; polyphosphates have been used for this purpose, but because phosphates are damaging to the environment zeolites are used in preference.
Calcium carbonate occurs naturally in two crystalline forms, calcite and the metastable aragonite. In calcite, the Ca2+ and [CO3]2- ions are arranged in such as way that each Ca2+ ion is 6-coordinate with respect to the carbonate O atoms, whereas in aragonite, each Ca2+ ion is surrounded by nine O atoms. The energy difference between them is <5 kJ mol-1 with calcite being the thermodynamically favoured form. However, aragonite is kinetically stable with respect to conversion to calcite. Aragonite can be prepared in the laboratory by precipitation of CaCO3 from hot aqueous solution.
Hydrated calcium sulfate (CaSO4.2H2O, gypsum) occurs naturally and is also a product of desulfurization processes involving Ca(OH)2 or CaCO3. Gypsum crystals cleave easily owing to the presence of layers which are held together by hydrogen bonding. When gypsum is heated at ≈ 400 K, it forms the hemihydrate CaSO4. 1/2H2O (plaster of Paris), and if this is mixed with water, the material expands slightly as the dihydrate is regenerated.
Barium sulfate is a sparingly soluble salt (Ksp = 1.07 × 10- 10) and the formation of a white precipitate of BaSO4 is used as a qualitative test for the presence of sulfate ions in aqueous solution.
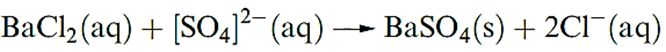
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















