

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Major predictions of kinetic theory
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 39
1-7-2017
1620
Major predictions of kinetic theory
- For a gas composed on N molecules,
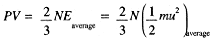 (1.1)
(1.1)
Comparing this with the ideal gas law, we have with N = nNA:
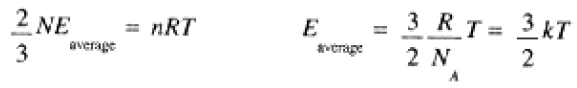 (1.2)
(1.2)
where k = R/NA, Boltzmann's constant, may be thought of as the gas constant per molecule.
(b) The distribution of speeds over the assemblage of molecules is given by an the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Figure 5-1 shows plots of the probability of finding an H2 molecule with speed u, as a function of u, at three different temperatures. The maximum of the distribution curve corresponds to the most probable speed, ump. The average speed, uavg, is slightly larger than ump. The root-mean-square speed, urms—the square root of (u2)average—is slightly larger than uavg. These measures of molecular speed are given by:
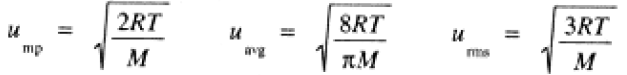 (1.3)
(1.3)
where M is the molar mass in kg/mol.
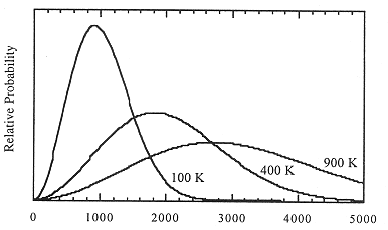
Figure 5-1. Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds for H2 at 100, 400, and 900 K.
Note that ump increases linearly with T1/2.
- The frequency of collisions per unit area of container wall is:
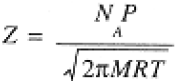 (1.4)
(1.4)
The rate at which a gas effuses (flows out) through a small hole in the container into a vacuum is exactly the rate at which the molecules would collide with a wall area equal to the area of the hole.
From Eq. (1.4), the effusion rates of two gases, both at the same pressure and temperature, are in the Ratio
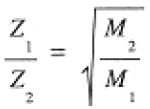 (1.5)
(1.5)
This relation is Graham's law of effusion: the ratio of the rates of effusion of two gases, at the same P and T, are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molar masses.
(d) Eq. (1.3)—average velocity is inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass—applies to other transport phenomena such as diffusion, thermal conduction, and nonturbulant flow.
Example 10
Calculate urms for H2 molecules at 100 K.
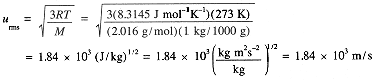 (1.6)
(1.6)
Example 11
Compute the relative rates of effusion of H2 and CO2 through a fine pinhole.
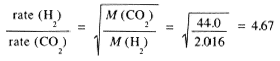 (1.7)
(1.7)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















